Figure 1.
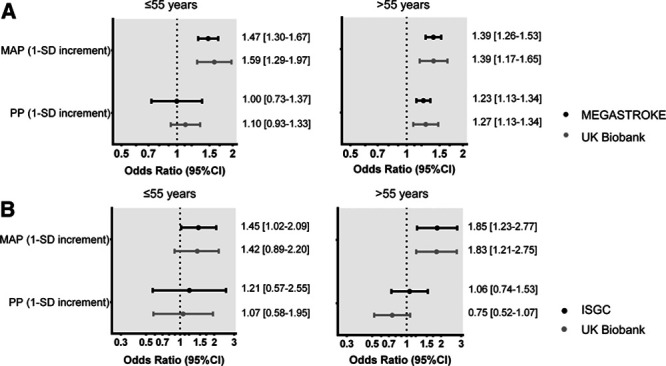
Associations of genetically predicted mean arterial pressure (MAP) and pulse pressure (PP) at age ≤55 and >55 y with risk of (A) ischemic stroke and (B) intracerebral hemorrhage. Effect sizes are derived from multivariable Mendelian randomization analyses adjusting for both genetically predicted MAP and PP in MEGASTROKE (primary sample, 60 341 cases, 454 450 controls) and the UK Biobank (validation sample, 3760 cases among 408 623 individuals). The analysis of the UK Biobank is based on incident events that occurred in individuals >55 y of age after the blood pressure measurements.
