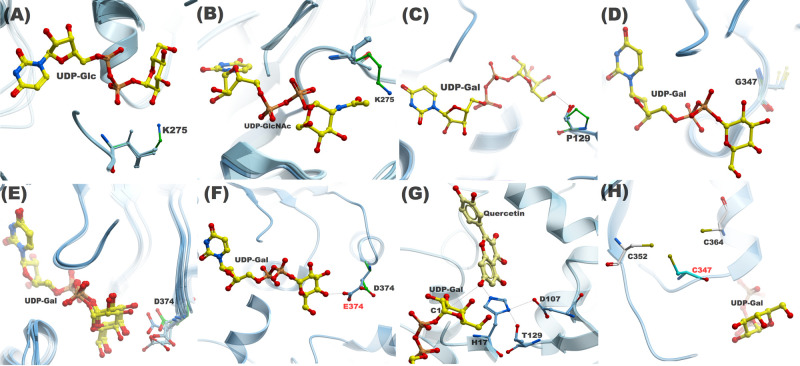
Figure 3. A structural comparison of WT and mutant residues investigated in this study.
The proximity of K275 (green) side chain in C1 loop to (A) Glc C2–OH and (B) NAc group in 76E4; (C) P129 on N5 loop in 76D1 is unable to make hydrogen bond with the donor sugar due to the absence of the OH group; (D) Spatial position of G347 on C4 loop in 76D1; (E) Asp or Glu is present in C5 loop at equivalent position of D374 (76E2) in other group H AtUGTs; (F) D374 side chain in 76E2 is unable to make hydrogen bond with the donor sugar. The side chain extended by one carbon atom to E374 enables the formation of a hydrogen bond; (G) The role of T129 in UDP-Gal recognition in 76D1 P129T mutant. T129 interacts with H17 and is involved in the formation of a catalytic triad, which is essential to glycosylation activity; (H) The proximity of C347 side chain to C352 and C364 side chains, where the Cys residues can potentially form a disulfide bond.