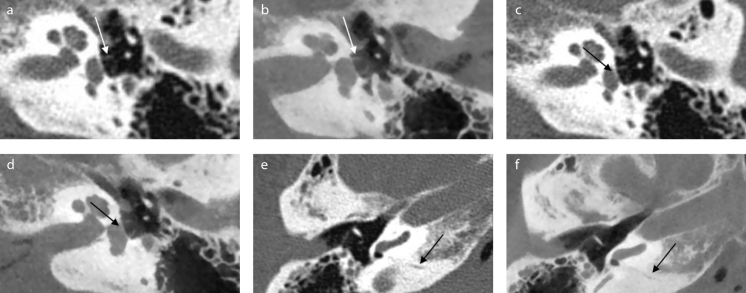
Figure 1. a–f.
Example of corresponding images of multislice computed tomography (MSCT) and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Images of MSCT (a, c, e) and corresponding images of CBCT (b, d, f ). In these images stapes crurae, footplate, and cochlear aqueduct are clearly visible on CBCT. (a, b) Crurae of stapes (axial view). (c, d) Footplate (axial view) (e, f ) Cochlear aqueduct (axial view). Cadaver heads were scanned in slightly different angles, because of which, the corresponding images might be in slightly different planes. During the assessment, images were turned and tilted for optimal comparison.