Fig. 7.
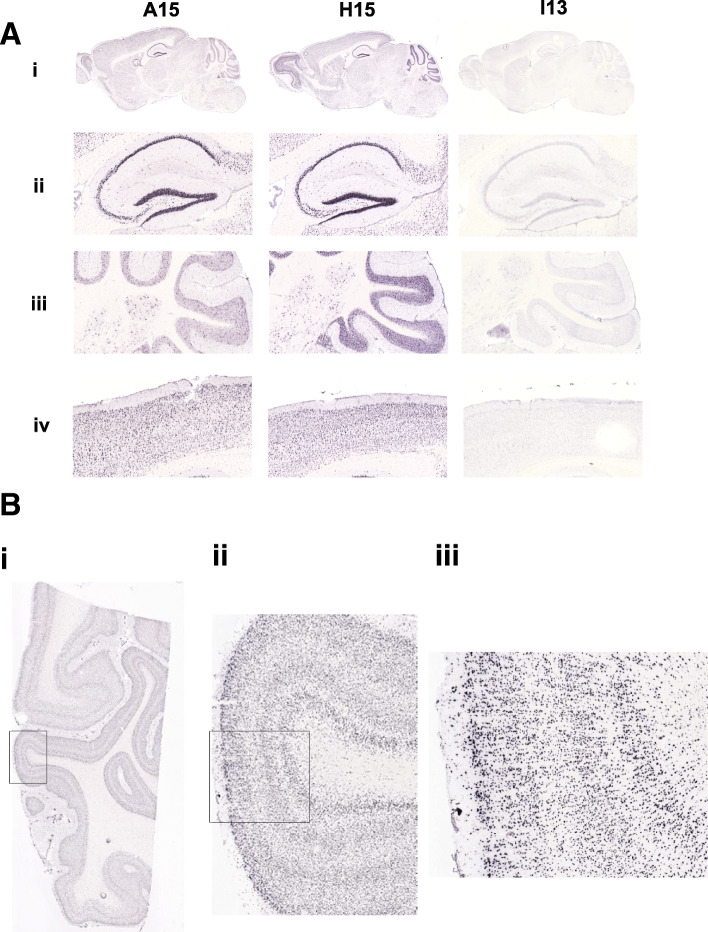
In situ hybridization of NPIP transgenic lines in brain tissue. a The transgenic line is indicated in each column (A15 (human), H15 (human), and I13 (baboon), respectively) and a representative sagittal section from each transgenic line is shown. (i) Expression of NPIP is undetectable in I13. (ii) Expression in hippocampal subregions. High expression is evident in the hippocampus pyramidal cells for both the A15 and H15 lines (derived from human BAC integrations). (iii) Cerebellar expression. High, widespread expression is apparent in the cerebellar granule cells and molecular layer in H15. In A15, large scattered cells in the granule layer are expressing NPIP. (iv) Examples of cortical expression patterns. High, widespread expression is evident in the cortex for both the A15 and H15 lines. b In situ hybridization of NPIP to human visual cortex. Human visual cortex, containing Brodmann’s areas 17 and 18, is shown hybridized to the riboprobe to the NPIP in the H15 transgenic line. Strong widespread expression is clearly visible throughout the visual cortex gray matter (ii and iii) as well as the white matter (i)