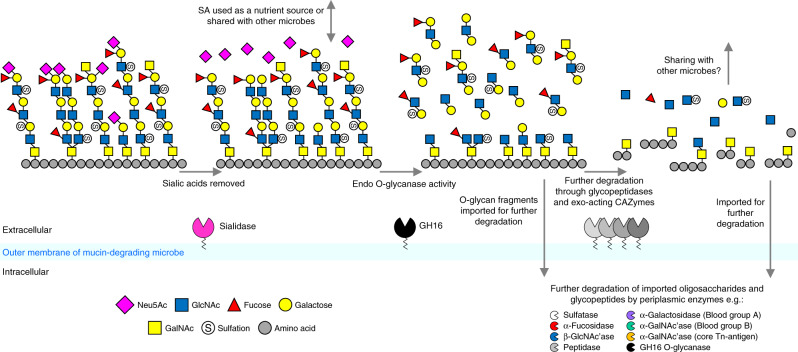
Fig. 8. Model for the role of GH16 O-glycanases in mucin breakdown.
A model of the initial steps of mucin degradation on the surface of Bacteroides spp. and A. muciniphila. Sialic acid is removed by surface-localised sialidases and the GH16 enzymes remove oligosaccharides for import into the periplasm for further degradation by other CAZymes, including periplasmic GH16 O-glycanases. In Bacteroides species, glycan import is via energy dependent SusCD-like complexes, but in A. muciniphila the mechanism of glycan import across the outer membrane is unknown. The remaining mucin glycoprotein is likely further degraded by other extracellular CAZymes and glycopeptidases19,29,50.