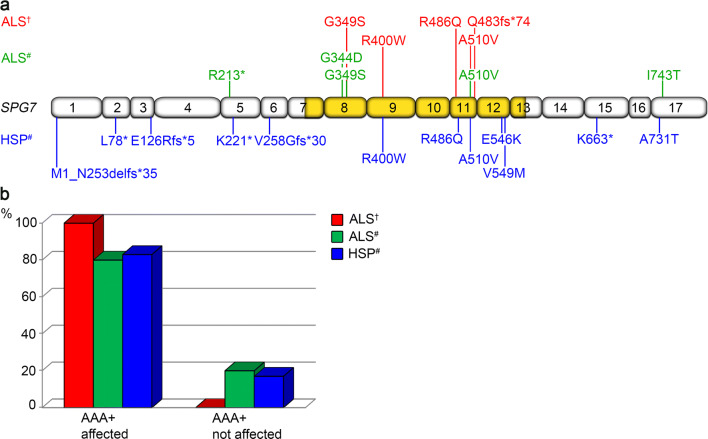
Fig. 3.
Overview of rare heterozygous deleterious SPG7 variants reported in ALS or HSP. a Summary of rare [MAF < 1% in Europeans (non-Finnish) according to the ExAC database] SPG7 variants predicted to be deleterious by at least one of two prediction tools, i.e. SIFT or PolyPhen-2, identified in ALS and HSP cases in a heterozygous state in our study and previously. The schematic illustration depicts all 17 exons of the SPG7 gene, whereby the genomic region encoding the AAA+ domain is highlighted in gold. Variants identified in ALS patients from our cohort are given in red. Variants previously described in ALS patients [26, 27, 38] are shown in green, and variants previously reported in HSP patients [12, 19, 39, 40] are indicated in blue. Protein sequence variants are given according to the Human Genome Variation Society recommendation v15.11. The exon structure of the SPG7 gene (NM_003119.2) was based on Alamut Visual Version 2.8. b The majority of rare heterozygous deleterious SPG7 variants in ALS and HSP patients affect the AAA+ domain that couples ATP hydrolysis to protein remodeling, i.e. 5/5 (100%) identified in ALS patients of our study, 4/5 (80%) previously described in ALS patients [26, 27, 38], and 10/12 (83%) previously detected in HSP cases [12, 19, 39, 40]. †—variants identified in our study. #—variants previously described. AAA+ domain ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities domain, ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, HSP hereditary spastic paraplegia