Fig. 1.
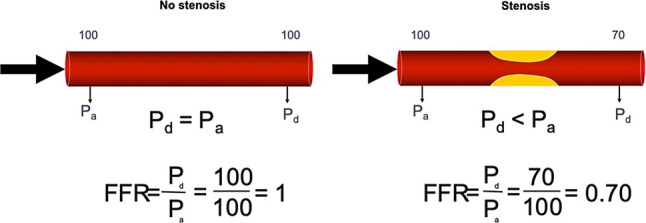
Concept of fractional flow reserve (FFR). FFR is defined as the ratio of mean proximal to mean distal coronary pressure. When no epicardial stenosis is present (left panel), the pressure loss across the coronary artery is negligible, and proximal aortic pressure (Pa) and distal coronary pressure (Pd) are equivalent, leading to an FFR of 1. In the presence of a stenosis (right panel), pressure loss across the stenosis will occur, and distal coronary pressure will be lower than proximal coronary pressure, leading to an FFR smaller than 1.0. In this example, the stenosis leads to a pressure gradient across the stenosis of 30 mm Hg, leading to an FFR of 0.70
