Fig. 3.
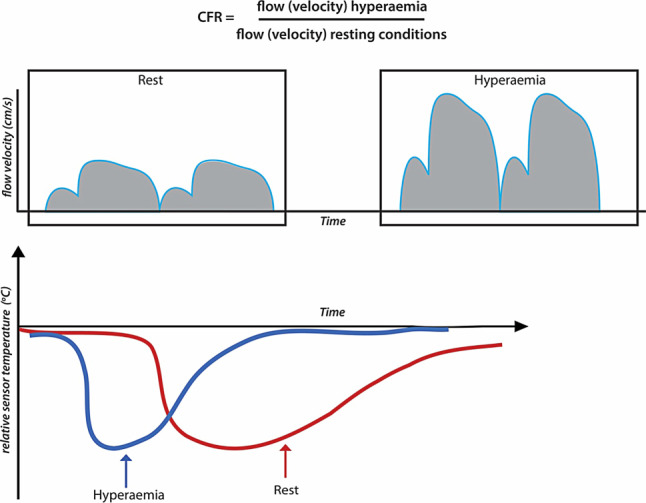
Coronary flow (velocity) reserve. Coronary flow (velocity) reserve (CFR) is defined as the ratio of hyperaemic to resting coronary flow (velocity). Coronary flow can be measured using the Doppler flow velocity technique (upper panel), and the coronary thermodilution technique (lower panel). The Doppler technique displays temporal changes in instantaneous peak coronary flow velocity, represented by the blue line in the schematic. The average peak coronary flow velocity over several cardiac cycles is used for the calculation of CFR. The thermodilution technique displays the individual thermodilution curves of a bolus of room-temperature saline. For thermodilution-derived flow measurements, the thermodilution curves are obtained in triplicate in resting and hyperaemic conditions. The mean transit time is calculated from these curves, and is average over three bolus injections in resting conditions, and three bolus injections in hyperaemic conditions for the calculation of CFR
