Fig. 4.
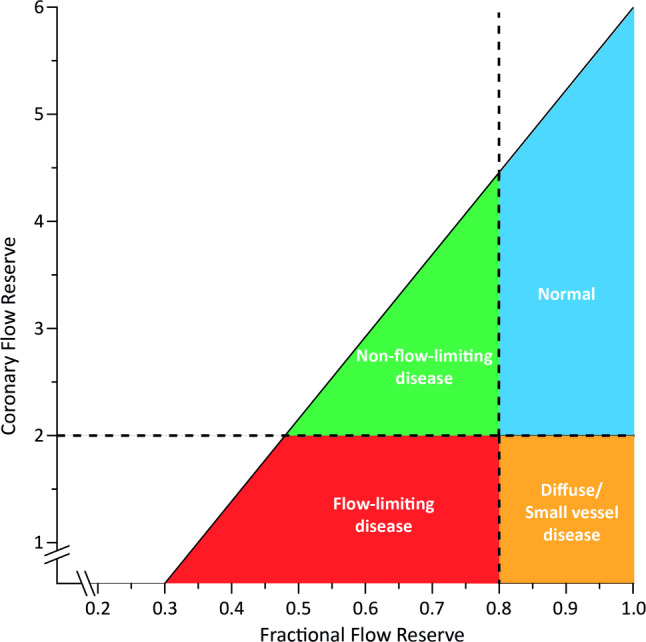
Conceptual plot of the fractional flow reserve (FFR)—coronary flow reserve (CFR) relationship. Four main quadrants can be identified by applying the clinically applicable cut-off values for FFR and CFR, indicated by the dotted lines. Patients in the upper right blue area are characterised by concordantly normal FFR and CFR, and patients in the red lower left area are characterised by concordantly abnormal FFR and CFR. Patients in the upper left green area and lower right orange area are characterised by discordant results between FFR and CFR, where the combination of an abnormal FFR and a normal CFR indicates predominant focal epicardial, but non-flow-limiting, coronary artery disease, and the combination of a normal FFR and an abnormal CFR indicates predominant microvascular or diffuse epicardial involvement in coronary artery disease. Adapted from Van de Hoef et al. [52] with permission of Wolters Kluwer Health
