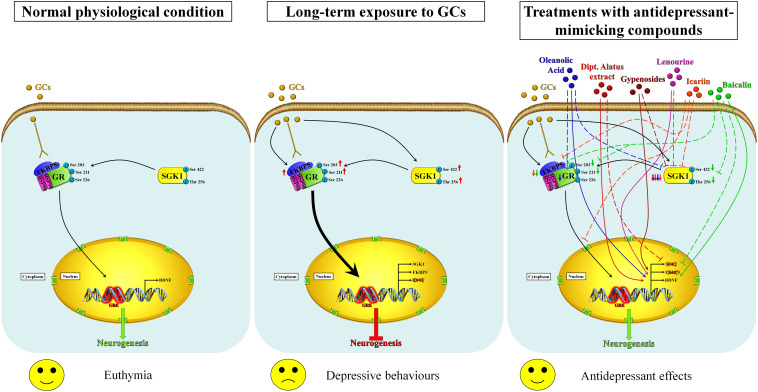
FIGURE 1.
Proposed mechanisms of action of nutraceuticals in the restoration of neurogenesis by modulating the GR/SGK1 signaling pathway. In the normal physiological state, the exposure of neuronal cells to basal levels of glucocorticoids activates GR and promotes its translocation into the nucleus, regulating thus neurogenesis (left panel). Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of glucocorticoids increases the expression of FKBP5, which impairs cytosolic GR binding capability and therefore the ultra-short negative feedback loop on GR sensitivity, increasing thus the negative effects of glucocorticoids. Furthermore, high glucocorticoids levels also improve SGK1 activity by increasing the phosphorylation of SGK1 at Ser422 and Thr256, which in turn causes the phosphorylation of GR at Ser203 and Ser211. The hyperphosphorylation of GR stimulates its nuclear translocation (thick arrow) and, by binding unidentified co-repressor factors, down-regulates the BDNF expression that results in impaired neurogenesis and then in depressive-like behaviors (middle panel). Nutraceuticals may counteract the effects of long-term exposure to glucocorticoids by restoring normal GR/SGK1 signaling through similar molecular mechanisms that lead to improved neurogenesis and antidepressant effects (right panel). Inhibitory and enhancing actions are indicated by dashed lines and arrows, respectively. Baicalin (green) is able to counteract the GCs-induced effects by enhancing the BDNF expression, downregulating the expression of SGK1, decreasing the FKBP5 protein levels as well as the phosphorylation rate of both GR and SGK1. Icariin (orange) decreases the SGK1 and FKBP5 protein levels and affects the GR nuclear translocation. Lenourine (violet) stimulates the BDNF expression whereas negatively regulates the SGK1 expression. Gypenosides (brown) reduces the SGK1 protein levels and enhances the BDNF expression. Dipt. Alatus extract (red) normalizes the mRNA levels of SGK1 and stimulates the expression of BDNF. Oleanolic acid (blue) down-regulates the expression of both SGK1 and GR as well as up-regulates the expression of BDNF.