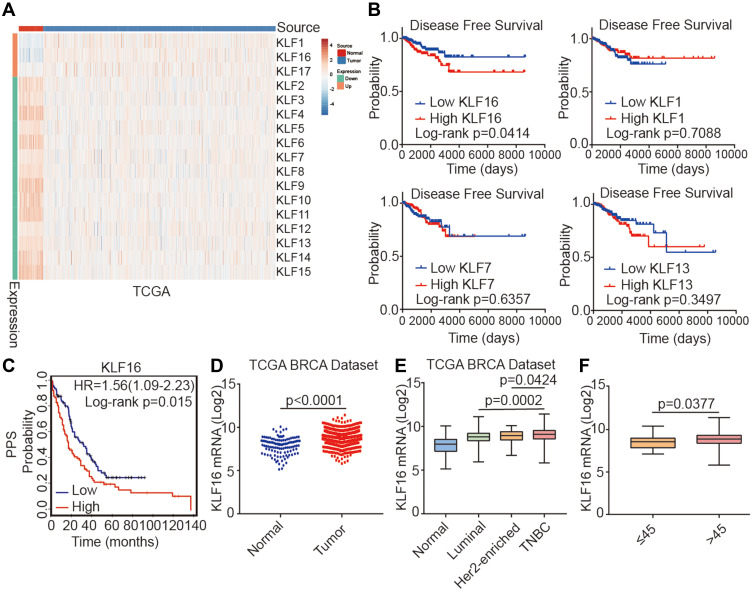
Figure 1.
Identification of KLF16 as a potential oncogene in breast cancer. (A) Heatmap showing the expression levels of KLF family members in normal breast tissues and cancer tissues in the TCGA BRCA dataset (normal, n=114; tumor, n=1086; t-test, p<0.001). (B) Survival plots showing disease-free survival (DFS) of breast cancer patients according to the expression levels of KLF16, KLF1, KLF7, and KLF13 (low, n=227; high, n=227; Log rank test). Data were acquired from the TCGA BRCA dataset and Quantile cut-off values were used to analyze disease-free survival. (C) Association between KLF16 (226328_at) expression levels and PPS of breast cancer patients (low, n=170; high, n=164; Log rank test). HR, hazard ratio; PPS, post-progression survival. (D) KLF16 mRNA expression levels in normal breast and tumor tissues (normal, n=114; tumor, n=1086; t-test). (E) KLF16 mRNA expression in different breast cancer molecular subtypes (normal, n=114; luminal, n=660; HER2-enriched, n=38; TNBC, n=177; t-test). (F) KLF16 mRNA expression in patients of different ages (≤45, n=27; >45, n=908; t-test).