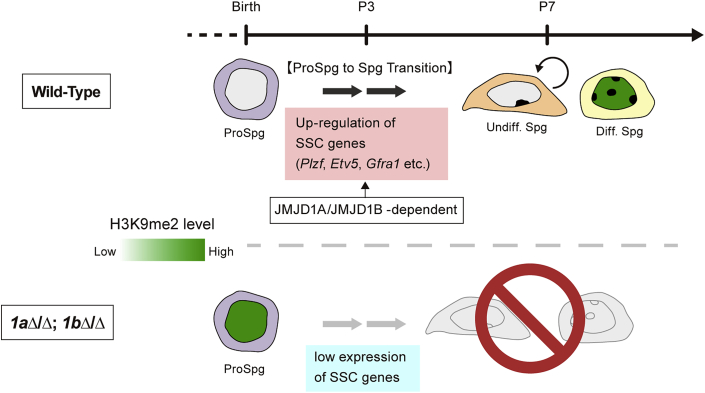
Figure 7.
Role of JMJD1A and JMJD1B in the Prospermatogonia to Spermatogonia Transition
In wild-type spermatogonia, JMJD1A and JMJD1B are highly expressed and the H3K9me2 mark is removed to extremely low levels in a JMJD1-dependent manner. This H3K9 hypomethylation status is critical for upregulation of SSC genes and the subsequent transition of prospermatogonia to spermatogonia after birth. In JMJD1A/JMJD1B-depleted spermatogonia, H3K9me2 is hypermethylated, resulting in low SSC gene expression and perturbed differentiation of prospermatogonia.