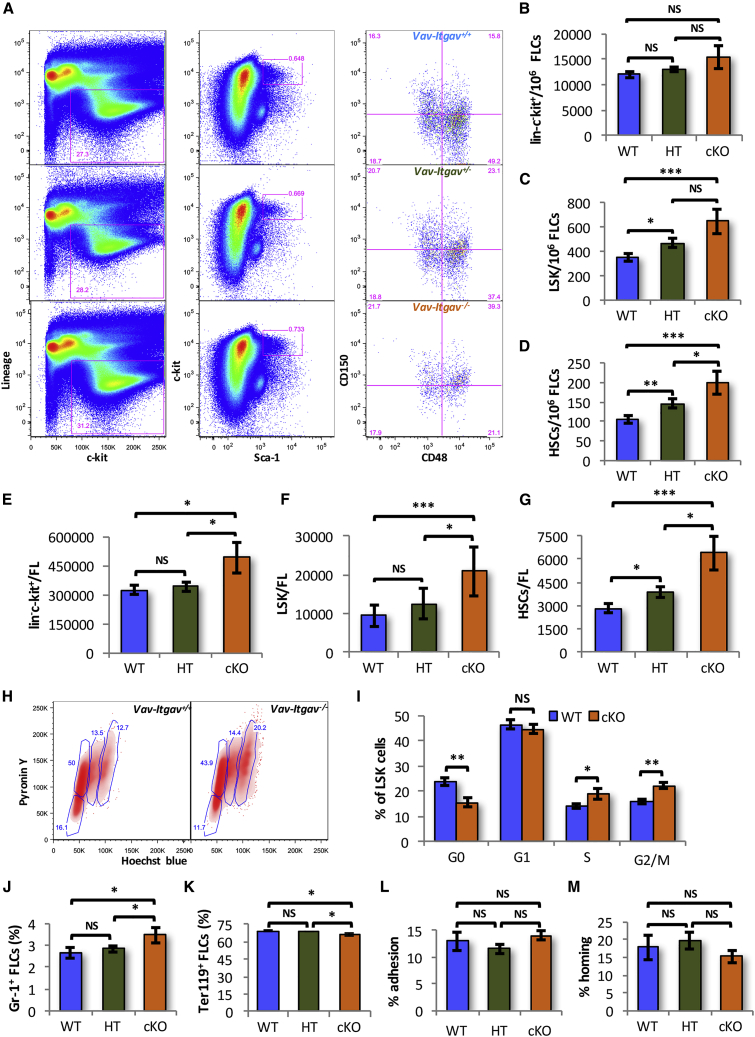
Figure 2.
Increased Frequency of Phenotypic HSCs in E14.5 Vav-Itgav−/− FL Tissues
(A) Vav-iCre and Itgavfl/fl mice were crossed to conditionally delete Itgav in hematopoietic system. The embryos were harvested at E14.5 and genotyped to identify Vav-Itgav+/+ (WT), Vav-Itgav+/− (HT), Vav-Itgav−/− (cKO) embryos. FL tissue was used for analysis of HSC frequency in by flow cytometry using specific antibodies.
(B–D) Quantification of frequency of various hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell populations in the FL tissue from WT, HT, and cKO embryos at E14.5; (B) lin−c-kit+ cells, (C) LSK cells, (D) primitive HSCs.
(E–G) Comparison of the total number of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells per FL from WT, HT, and cKO embryos at E14.5; (E) lin−c-kit+ cells, (F) LSK cells, (G) primitive HSCs. (H) Cell-cycle analysis of the LSK cells harvested from E14.5 FL tissues by Hoechst 33342/pyronin Y staining (n = 6).
(I) Comparison of the proportion of FL-derived LSK cells in various stages of cell cycle.
(J and K) Flow cytometry-based analysis performed to compare the frequency of lineage-committed cells in E14.5 FL tissue from WT, HT, and cKO embryos. (J) Granulocytes identified as Gr-1+ cells, (K) erythrocytes identified as Ter119+ cells.
(L) Adhesion potential of E14.5 Vav;Itgav+/+ (WT), Vav;Itgav+/- (HT), and Vav;Itgav−/− (cKO) FL-derived LSK cells was compared through in vitro adhesion assays. Freshly isolated LSK cells were allowed to adhere on ST2 cell feeder. The percentage of cells that adhered to the feeder after 3 h was plotted for each condition (n = 4).
(M) Whole FL cells from Vav;Itgav+/+ (WT), Vav;Itgav+/− (HT), and Vav;Itgav−/− (cKO) mice, were infused in lethally irradiated animals. The percentage of transplanted colony-forming cells that homed into the BM within 16 h was plotted (n = 2, N = 8).
An unpaired two-tailed Student's t test was performed. n = 2–4, N = 8–14, t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.005. See also Figures S2 and S3.