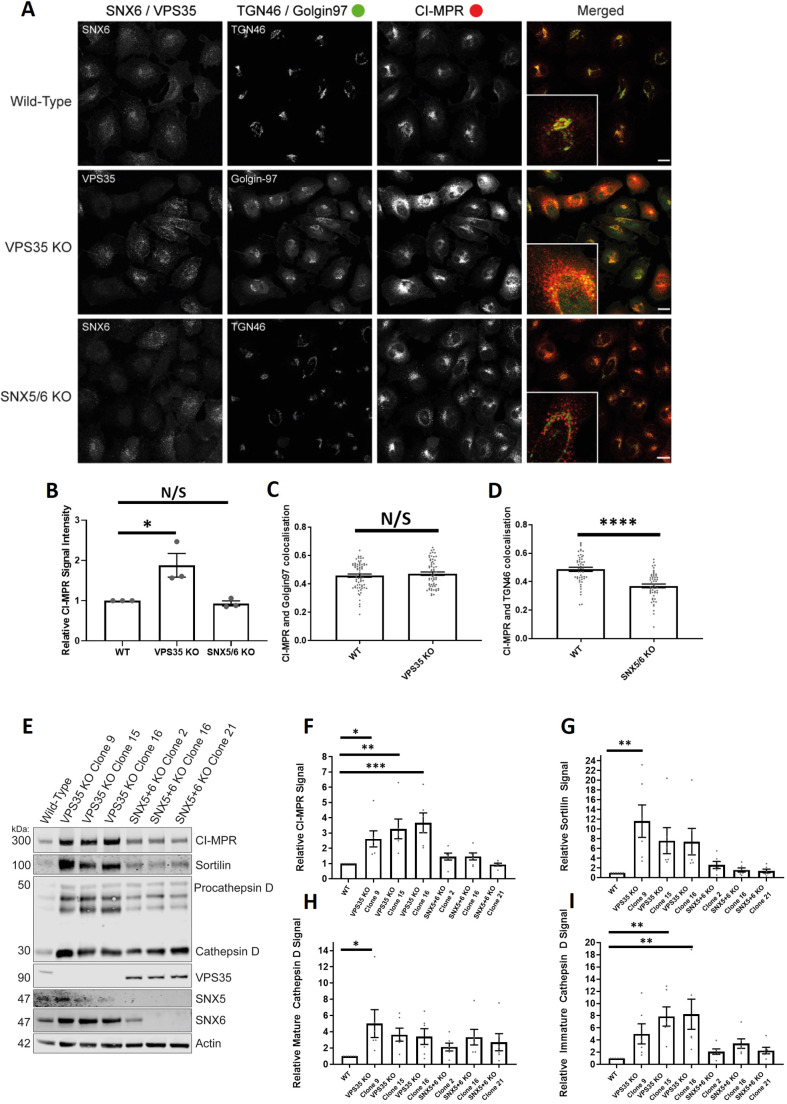
Fig. 7.
VPS35-knockout H4 neuroglioma cells display an upregulation of lysosomal hydrolases and lysosomal hydrolase receptors. (A) VPS35 and SNX5/SNX6 dual-knockout mixed population H4 neuroglioma cells were generated and then fixed. Cells were stained with either anti-VPS35 or anti-SNX6 antibodies to confirm which cells were knocked out in the mixed population. Cells were also co-stained with both anti-CI-MPR and either anti-TGN46 (SNX5/SNX6 dual knockout) or anti-Golgin97 (VPS35 knockout) antibodies. The merged panel displays both the CI-MPR and TGN46 or Golgin97 channels. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Normalised values for relative CI-MPR signal intensity between conditions. nexp=3, ncell=44–68 with average value data being shown for each experiment. P<0.05; N/S, not significant (P>0.05) (Student's t-test). (C) Pearson's colocalisation between CI-MPR and Golgin97 in wild-type and VPS35-knockout cells. nexp=3, ncell=64–69 with all data points being displayed. N/S, not significant (P>0.05) (Welch's t-test). (D) Pearson's colocalisation between CI-MPR and TGN46 in wild-type and SNX5/SNX6 knockout cells. nexp=3, ncell=49–53 with all data points being displayed. ****P<0.0001 (Welch's t-test). (E) Representative western blot analysis of wild-type and VPS35-knockout or SNX5/SNX6 knockout clonal cell lines using anti-CI-MPR, anti-sortilin, anti-cathepsin D, anti-VPS35, anti-SNX5, anti-SNX6 amd anti-actin antibodies. (F–I) Relative (actin) measured signals for wild-type and VPS35-knockout or SNX5/SNX6 dual-knockout clonal cell lines for CI-MPR, sortilin, mature cathepsin D and immature cathepsin D. n=7. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (ordinary one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons). Error bars show the s.e.m.