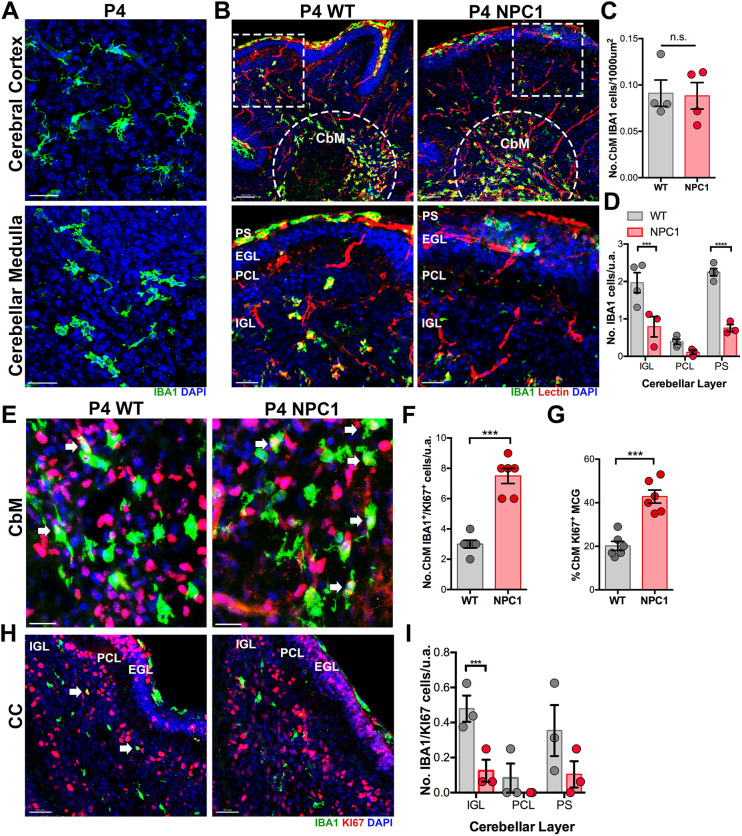
Fig. 2.
Decreased radial migration of microglial precursors in P4 Npc1nmf164 mice. (A) IBA1+ differentiating microglia in the cortex versus IBA1+ round/ameboid microglial precursors in the cerebellum at P4 in WT mice. (B) IBA1+ microglial precursors concentrated in the developing CbM of the cerebellum (dashed semicircle). IBA1+ microglial precursors are observed migrating radially toward the cerebellar cortex layers (IGL, PCL and EGL) following Tomato Lectin+ capillaries. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification below. (C) Quantification of IBA1+ cells in the developing CbM at P4. (D) Quantification of the number of IBA1+ cells in the IGL and PS at P4. (E) IBA1+ and KI67+ cells in the developing CbM at P4. (F) The number of IBA1+/KI67+ cells is significantly higher in the CbM of Npc1nmf164 mice. (G) The percentage of KI67+ microglia (MCG) is significantly higher in the CbM of Npc1nmf164 mice. (H) IBA1+ and KI67+ cells in the developing cerebellar cortex (CC) at P4. Arrows indicate IBA1+ cells that are KI67+. (I) The number of IBA1+/KI67+ cells is significantly lower in the IGL of Npc1nmf164 mice. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. n=3-4 mice. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. n.s., not significant; u.a., unit area. Scale bars: 50 µm (A,E,H); 100 µm (B, top row); 50 µm (B, bottom row).