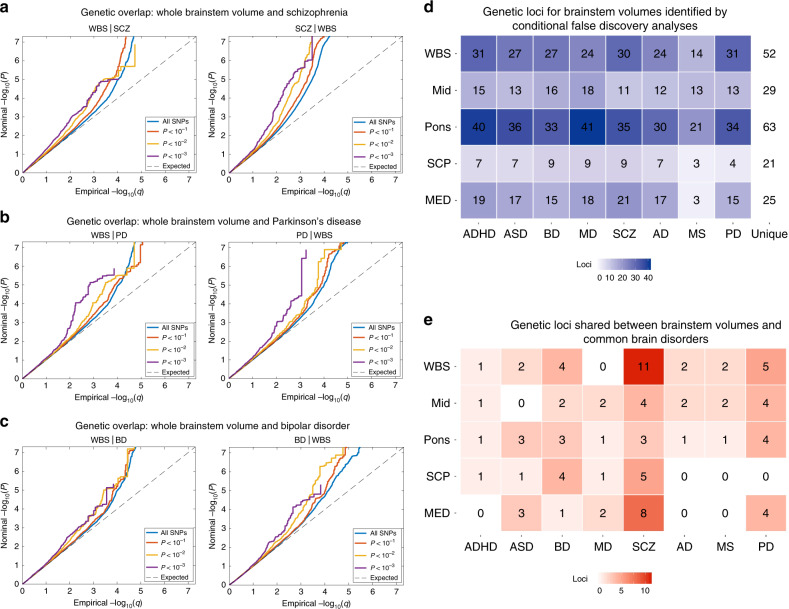
Fig. 3. Genetic overlap between brainstem volumes and common brain disorders.
a Conditional Q–Q plots for whole brainstem volume conditioned on SCZ (left) and vice versa (right), demonstrating genetic overlap. b Conditional Q–Q plots for whole brainstem volume conditioned on PD (left) and vice versa (right), showing genetic overlap between these phenotypes. c Conditional Q–Q plots for whole brainstem volume conditioned on BD (left) and vice versa (right), demonstrating genetic overlap. d Enhanced discovery of genetic loci for each of the brainstem volumes when conditional false discovery rate analyses were run for each of the brainstem volumes conditioned on the eight brain disorders. These analyses revealed a total of 208 genetic loci for whole brainstem volume, and 111, 270, 55, and 125 loci for volumes of the midbrain, pons, SCP, and medulla oblongata, respectively. These genetic regions were located in 52 unique genetic loci for whole brainstem volume, and 29, 63, 21, and 25 unique loci for volumes of the midbrain, pons, SCP, and medulla oblongata. e conjunctional false discovery rate analysis detected shared genetic loci across brainstem volumes and the eight clinical conditions. The largest numbers of shared loci were found for SCZ (31), BD (14), and PD (17), whereas 8, 4, 6, 9, and 5 genetic loci were jointly shared for ASD, ADHD, MD, AD, and MS, respectively, and the brainstem volumes, when applying a conjunctional FDR threshold of 0.05. WBS whole brainstem. MID midbrain. SCP superior cerebellar peduncle. MED medulla oblongata. ADHD attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. ASD autism spectrum disorders. BD bipolar disorder. MD major depression. SCZ schizophrenia. AD Alzheimer’s disease. MS multiple sclerosis. PD Parkinson’s disease.