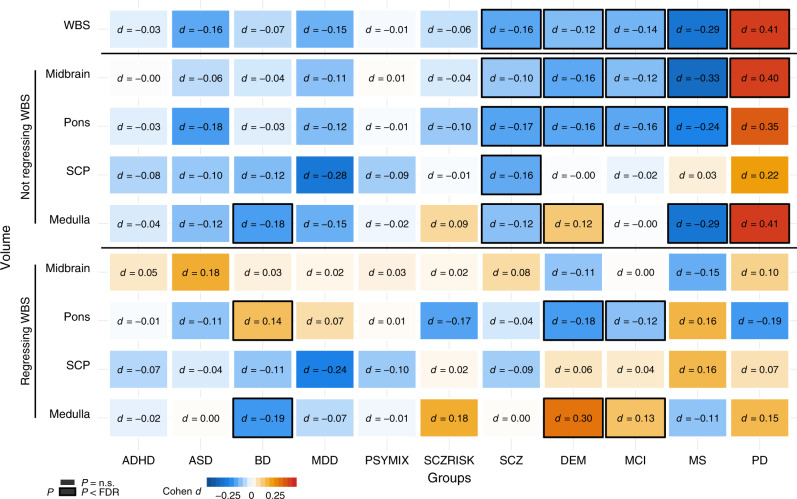
Fig. 5. Volumes of brainstem structures in individuals with common brain disorders compared with healthy controls.
Linear models were run covarying for sex, age, age², intracranial volume, and scanner site. The analyses for volumes of midbrain, pons, SCP, and medulla oblongata were run both with and without covarying for whole brainstem volume. The figure depicts the resulting case-control differences in Cohen’s d, whereas group differences in mm3 are presented in Supplementary Fig. 14. There were differential volumetric alterations in individuals with BD, SCZ, DEM, MCI, MS, and PD as indicated by black frames, after controlling for multiple testing using false discovery rate (Benjamini–Hochberg, accounting for all 99 tests). ADHD attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. ASD autism spectrum disorders. BD bipolar disorder. MDD major depressive disorder. PSYMIX non-SCZ psychosis spectrum diagnoses. SCZRISK prodromal SCZ or at risk mental state. SCZ schizophrenia. DEM dementia. MCI mild cognitive impairment. MS multiple sclerosis. PD Parkinson’s disease. WBS whole brainstem. SCP superior cerebellar peduncle. Medulla medulla oblongata.