Figure 5.
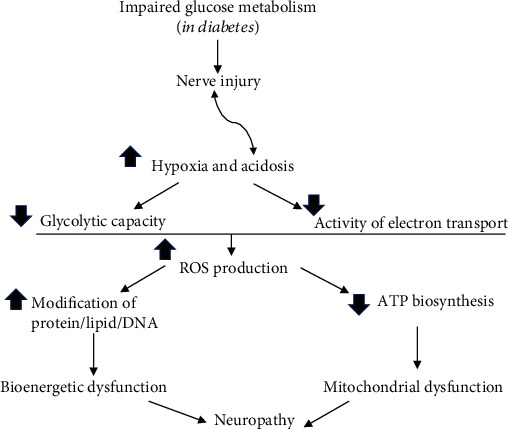
Summary of the major contributors to diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes-induced impairment of glucose metabolism causes hypoxia and acidosis, which contributes to and exacerbates the nerve injury. As a result, both glycolytic capacity and activity of electron transport chain are reduced, leading to overproduction of ROS, which, not only reducing ATP production but also initiating various modifications on protein/lipid and DNA. Thus, mitochondrial and bioenergetic dysfunction leads to neuropathy.
