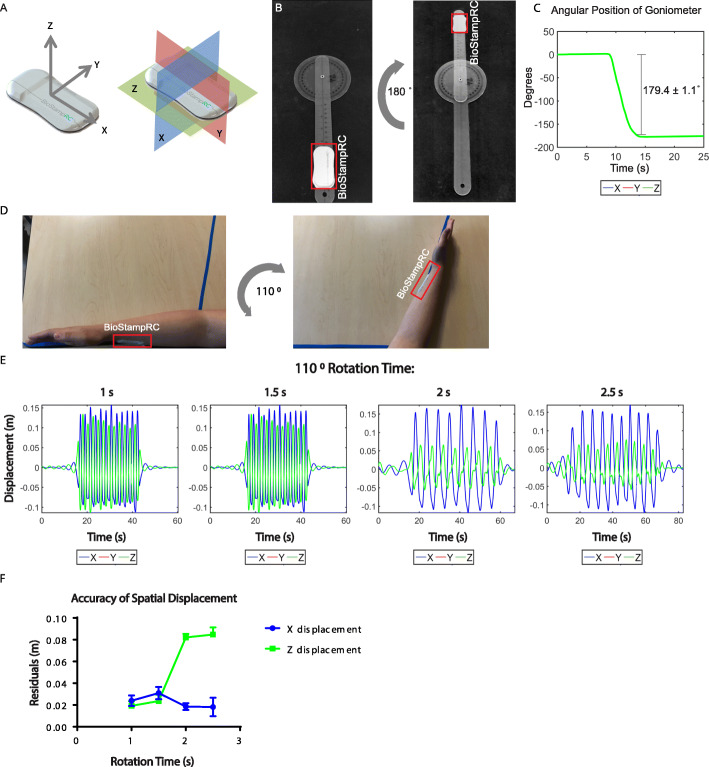
Fig. 2.
Characterization and Accuracy of BioStampRC. (a) Tri-axial orientation of the BioStampRC during acceleration and gyroscope recordings: x-plane (blue), y-plane (red), and zplane (green). BioStampRC image provided by MC10 Inc. (b) Top view of BioStampRC on distal end of goniometer on flat surface at starting position (left) and after 180 ° movement about BioStampRC z-axis. (c) BioStampRC angular position about z-axis after 180 ° movement on goniometer. Values shown as average degrees ± standard deviation (n = 3). (d) Top view of BioStampRC on distal volar surface of arm while on flat surface at starting position (left) and after 110 ° movement in the x-z plane, about y-axis. (e) Displacement output from BioStampRC accelerometer measurements after arm rotation at decreasing velocities (left to right). (f) Accuracy of X and Z displacement measurements at different rotational speeds. Values shown as average meters ± standard deviation (n ≥ 8)