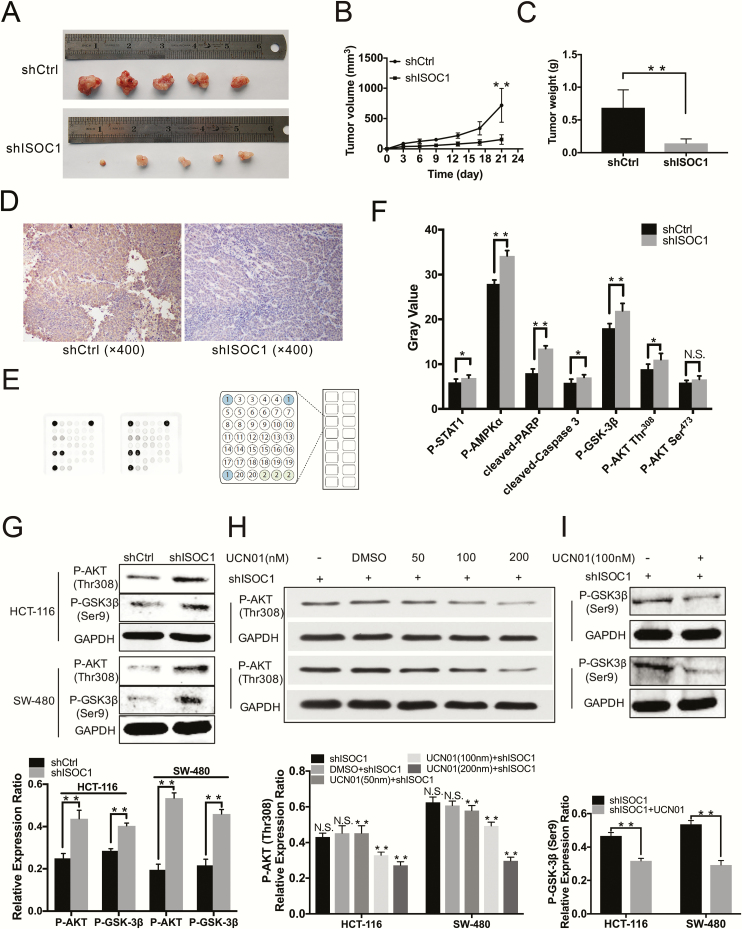
Figure 4.
Knockdown of ISOC1 inhibits colon cancer cell growth in vivo and alters signaling proteins in colon cancer cells. (A) The tumors at day 21. HCT-116 cells infected with NC (shCtrl) or ISOC1-shRNA (shISOC1) lentivirus were subcutaneously implanted into nude mice, and 21 days later, the tumors were excised. (B) Tumor volumes were calculated in each group every 3 days from day 1 to day 21. (C) Tumor weights were measured on day 21. The error bars represent the standard deviation; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (D) Representative immunohistochemical staining of ISOC1-shRNA (shISOC1) and NC (shCtrl) groups (×400). (E) PathScan assay. Eighteen pivotal signaling proteins were detected by the PathScan intracellular signaling array kit. (F) The upregulated proteins after silencing ISOC1. (G) Western blot assay. The protein levels of p-AKT Thr308 and p-GSK-3β Ser9 were increased in the shISOC1 group compared to the shCtrl group. (H, I) Western blot assay. The protein levels of p-AKT Thr308 and p-GSK-3β Ser9 decreased with UCN01 treatment (100/nM) in ISOC1 knockdown cells. The error bars represent the standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.