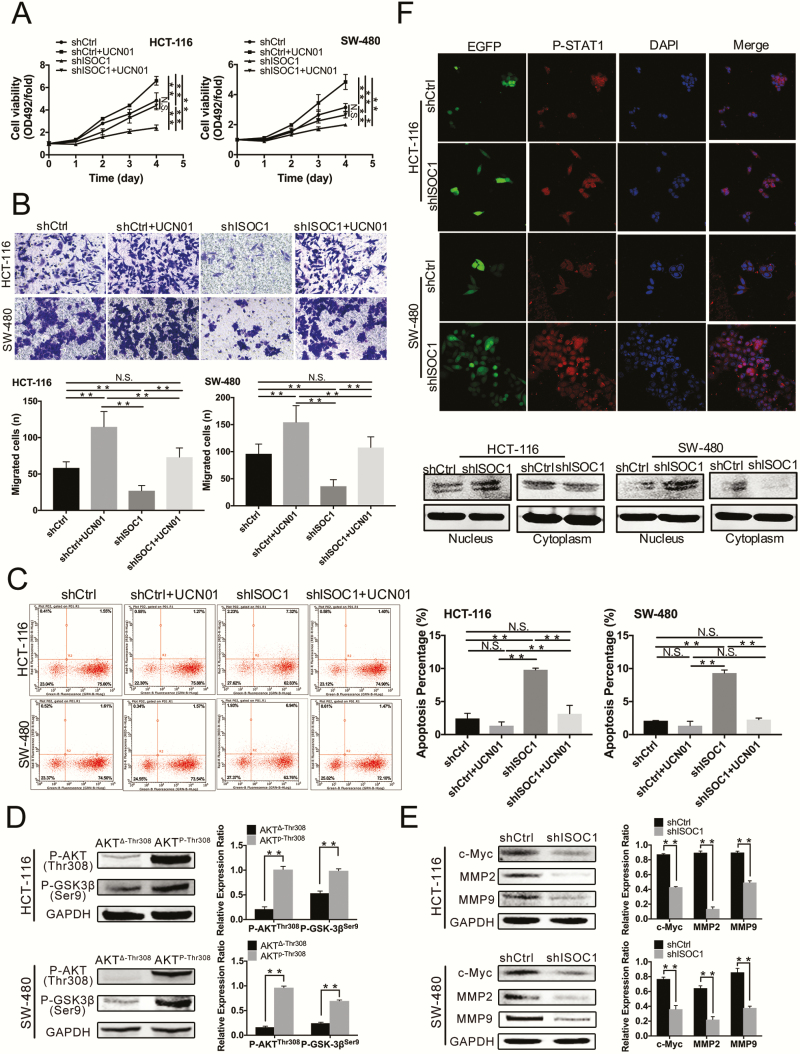
Figure 5.
The effects of ISOC1 knockdown on the biological function of colon cancer cells are rescued by UCN01. Further verification of the mechanism of ISOC1 in colon cancer cells. The protein level of p-STAT Tyr701 in colon cancer cell nuclei was increased by ISOC1 knockdown. (A) MTS assays. (B) Transwell migration assays. (C) Cell apoptosis assay. (D) Western blot assay. The protein level of p-GSK-3β Ser9 was upregulated by overexpression of p-AKT Thr308. AKTΔ-Thr308: p-AKT Thr308 deletion plasmid. AKTP-Thr308: p-AKT Thr308 activation plasmid. (E) Western blot assay. The protein levels of c-Myc, MMP2 and MMP9 were significantly reduced by ISOC1 knockdown. (F) Confocal microscopy and western blot analysis of p-STAT1 Tyr701 nuclear localization. Green signals represent cells infected with lentiviruses. DNA was visualized with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Western blot analysis showed that the protein levels of p-STAT1 Tyr701 were increased in the shISOC1 group compared to the shCtrl group. The error bars represent the standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.