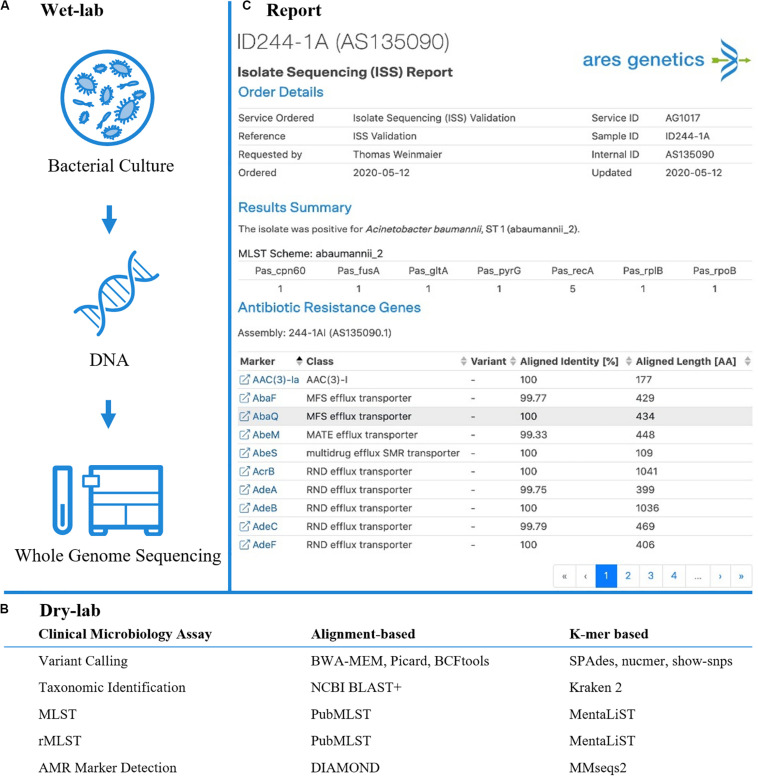
FIGURE 1.
Established and validated workflow for WGS from bacterial isolates. (A) A state-of-the-art wet-lab workflow for processing of bacterial isolates was implemented. (B) Dry-lab analysis of WGS data was evaluated using alignment-based and k-mer based bioinformatics tools for clinical microbiological assays (including variant calling, taxonomic identification, MLST, rMLST, AMR marker detection). For AMR marker detection, AMR markers with associated performance indicators were used as accessible via the QIAGEN CLC Microbial Genomics ARESdb Module (https://resources.qiagenbioinformatics.com/manuals/clcmgm/current/index.php?manual = ARES_Database.html). (C) The analysis report as provided via ares-genetics.cloud, including results for taxonomic identification, subtyping and AMR marker detection (illustrated for validation sample ID244-1A).