Fig. 3.
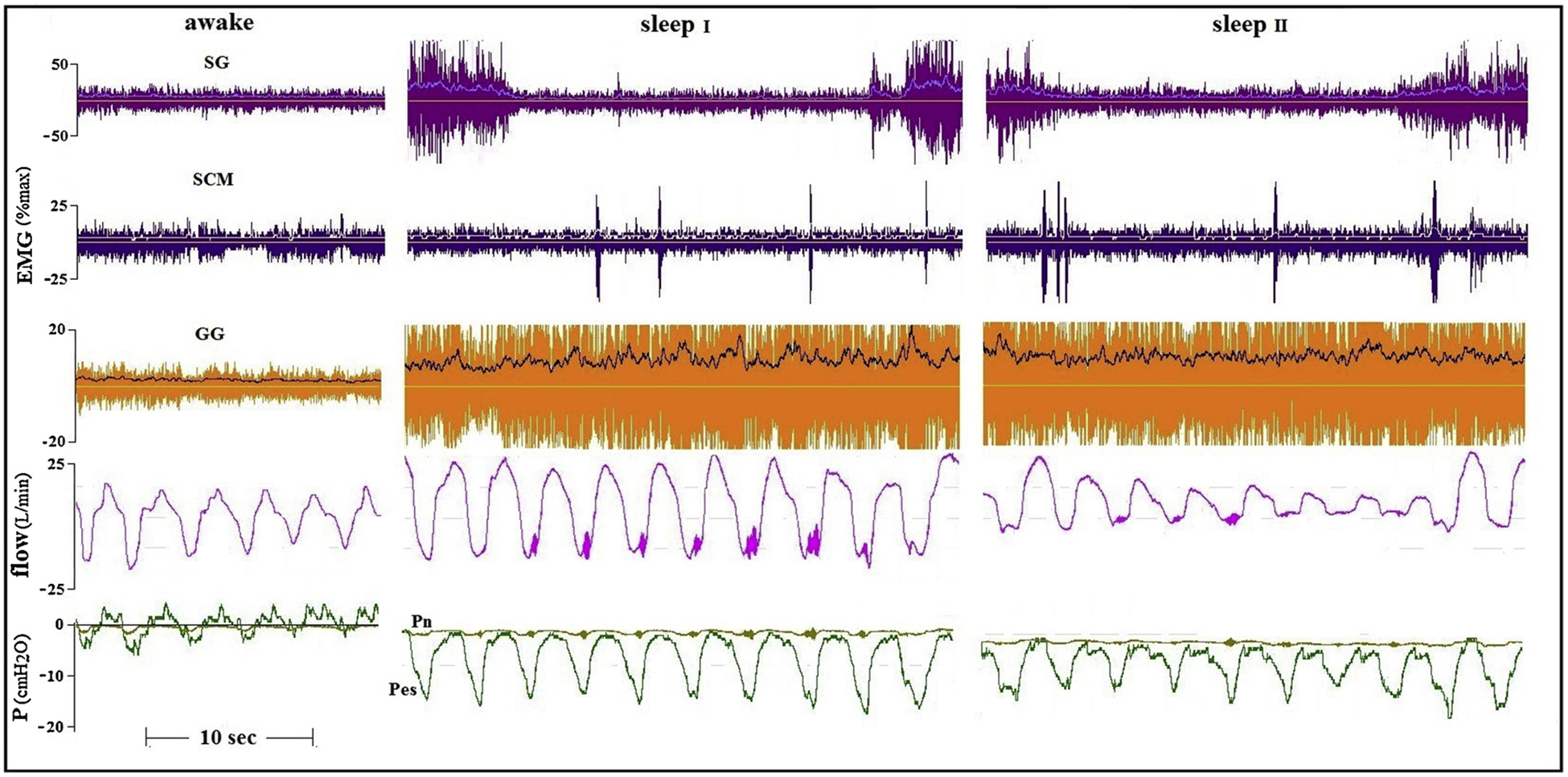
Awake and two sleep tracings of a younger (21 yrs) healthy subject. In this subject CNAP mainly increased tonic activity of the GG. However, only the intermittent co-activation of the SG was associated with disappearance of flow vibrations (sleep I, Pn= −2cmH2O) and also abolished flow limitation (sleep II, Pn= −4cmH2O) without arousal.
