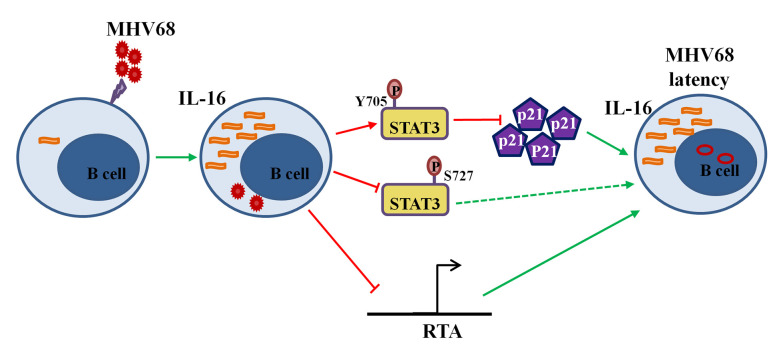
Fig 12. Working model of IL16 function during MHV68 infection.
MHV68 infection induces IL16 production, which, in turn, increases STAT3(Y705) phosphorylation, subsequently reduces p21 expression, and inhibits MHV68 reactivation. Meanwhile, IL16 partially inhibits RTA promoter activity and STAT3(S727) phosphorylation, contributing to the inhibition of MHV68 reactivation. Ultimately, MHV68-induced IL16 helps to maintain MHV68 latency.