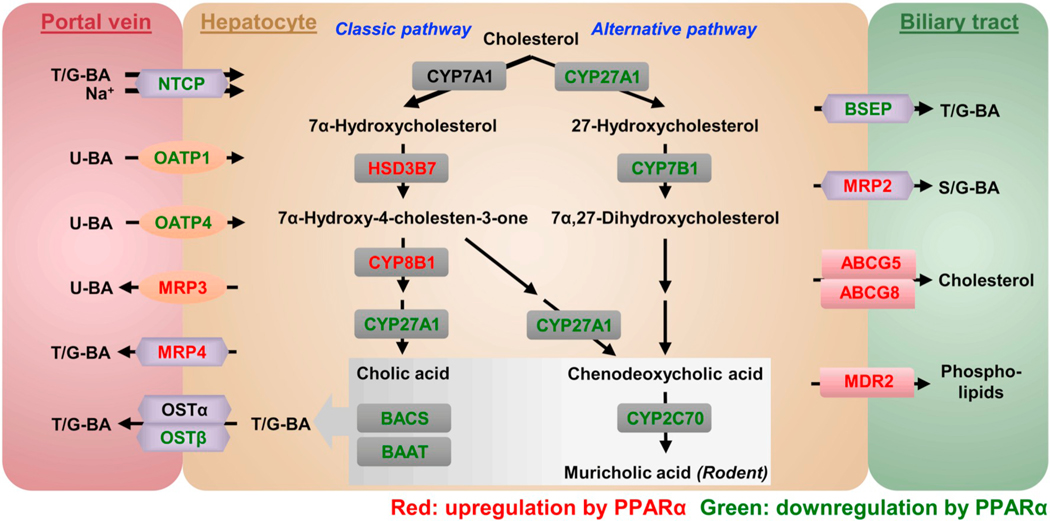
Fig. 9.
Mechanism for hepatocyte PPARα activation on BA synthesis and transport regulation. PPARα activation within hepatocytes by Wy represses both hepatic BA uptake mediated by NTCP and OATPs and canalicular BA efflux mediated by BSEP, while increases sinusoidal BA efflux by induction of MRP3 and MRP4. The overall effect is elevated circulating BAs. PPARα activation also induces the expression of CYP8B1 which leads to the increased levels of CA and TCA in classic pathway as well as downregulates the expression of CYP27A1 and CYP7B1 in alternative BA synthesis. These changes result in an increased 12α-OH/non-12α-OH BAs ratio. The reduced expression of CYP2C70 decreases the synthesis of FXR antagonist pool consisting of TαMCA and TβMCA. T/G-BA, taurine/glycine-conjugated BA. U-BA, unconjugated BA. S/G-BA, sulfate or glucuronide-conjugated BA. The proteins in red are induced by PPARα activation and the proteins in green are suppressed by PPARα activation. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)