Fig. 5. h4E-BP1 HyperTRIBE identifies h4E-BP1 targets in PC3 cells.
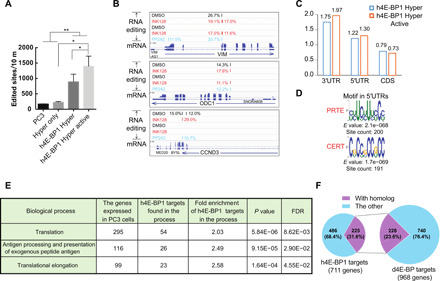
(A) The number of edited sites is significantly higher in h4E-BP1 HyperTRIBE than in wild-type PC3 cells or in Hyper only. The number of edited sites was increased after Ink128 or PP242 treatment (h4E-BP1 Hyper Active). Expressing hyperADARcd alone (Hyper only) did not result in more editing sites than in control PC3 cells. N = 2 to 3, +SEM; *P < 0.05, paired one-tailed Student’s t test; **P < 0.005, unpaired one-tailed Student’s t test. (B) IGV view of three examples of the editing sites and editing percentages of mTOR-sensitive genes VIM, ODC1, and CCND3. Background editing sites detected in control PC3 cells or Hyper only were removed. Samples were incubated with DMSO (black), Ink128 (red), or PP242 (blue). The alignment of mRNA-seq reads is also shown. (C) The editing sites of h4E-BP1 HyperTRIBE are enriched in 5′UTR and 3′UTR of mRNA. (D) Consensus motifs from the 5′UTRs of 711 h4E-BP HyperTRIBE targets (listed in table S4). These targets were detected at least twice after mTOR inhibition. (E) Table of enriched GO term biological processes in 711 h4E-BP1 HyperTRIBE targets. (F) Ortholog mapping between 711 h4E-BP1 HyperTRIBE targets and 968 Thor-HyperTRIBE targets shows that 32% of h4E-BP1 targets are conserved in Drosophila.
