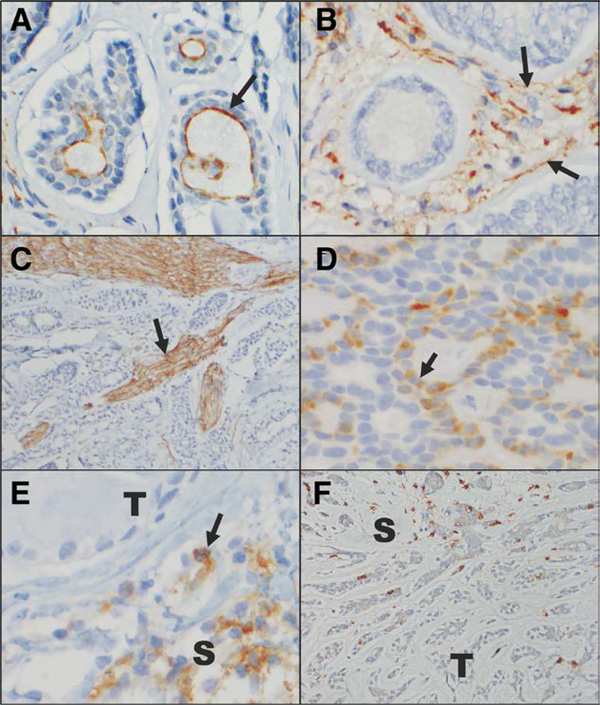
FIG. 1.
Immunohistochemical staining for PD-L1, PD-L2, and CD8 in adenoid cystic carcinoma. A, PD-L1 positively immunnonstains the apical membranes of some tumor cells (arrow). B, PD-L1 positively immunostains the stromal cells (arrow) surrounding some tumors. In this case, the tumor cells do not express PD-L1. C, This anti-PD-L1 antibody also prominently highlights nerve fascicles in a number of the tumor samples examined (arrow). D, PD-L2 positively immunostains the cytoplasm and membranes of some tumor cells (arrow). E, PD-L2 positively immunostains clusters of S. In this case, the T do not express PD-L2. F, Rare CD8-positive T-lymphocytes are present infiltrating the tumor, but greater numbers are appreciated in the surrounding stroma (A–F, immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, original magnification ×40, ×40, ×10, ×40, ×40, ×20, with additional optical magnification of ×3 for A–E and ×2 for F). PD-L, programmed cell death ligand; S, stromal cells; T, tumor cells.