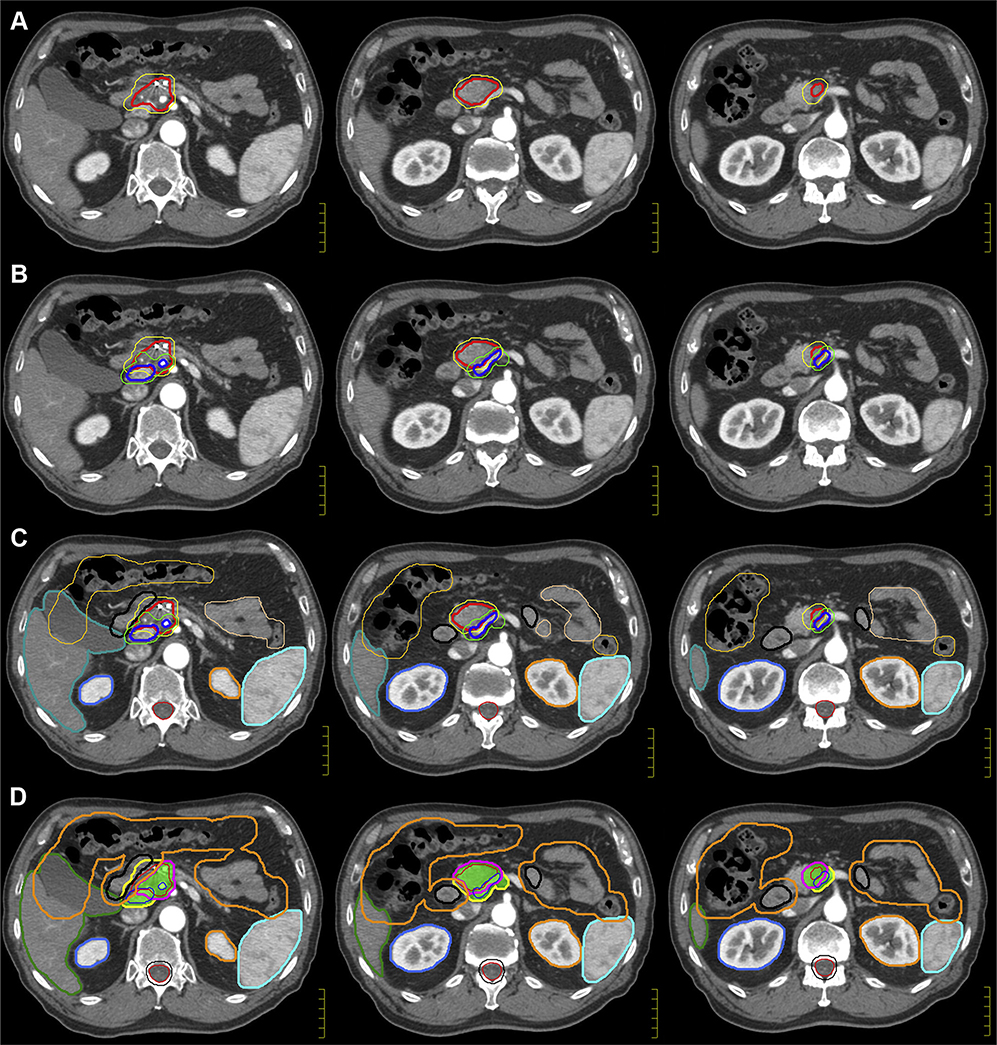
Figure 5.
Case 2: Target volume creation (internal gross tumor volume and TVI) and planning volume creation (organ at risk, planning target volume, and planning organ-at-risk volume). (A, B) Similarly to the hypofractionated approach, contours from the appropriate phases should be considered to create an iGTV (red). For stereotactic body radiation therapy, the TVI should be contoured (blue). The TVI encompasses any portion of the vessel with direct contact to tumor. These involved vessels should be contoured to the full radial extent when abutting tumor (eg, in the extent of 180° abutment, the full 360° extent of a vessel will be included). The superior and inferior extent of the TVI should be delineated on all axial slices on which iGTV is contoured and will also be expanded by 3 mm (green). In this patient, given contact of the pancreatic head mass with the common hepatic and splenic artery, these contoured vessels represent the TVI. (C, D) A 2-volume approach is used for planning that considers iGTV (red), the TVI (blue), and GI PRV (orange). GI PRV represents a 5-mm expansion from all bowel structures, including the small (peach) and large (apricot) iBowel. PTV_Low (yellow) represents the low-dose level at 3300 cGy and encompasses a 3-mm expansion of both, the iGTV, and TVI to ensure minimum dose encompasses these structures without regard to normal structures. As with the 15-fraction regimen, a modified, high-dose planning volume, zPTV_High (green color wash), is created from (iGTV + TVI) + 3 mm with the GI PRV subtracted. Essentially, the PTV_Low modified by the luminal organs at risk represents the targeted area for maximum dose (5000 cGy) to the tumor and TVI. Abbreviations: GI PRV = gastrointestinal planning organ-at-risk volume; iGTV = internal gross tumor volume; TVI = tumor–vessel interface.