Figure 1.
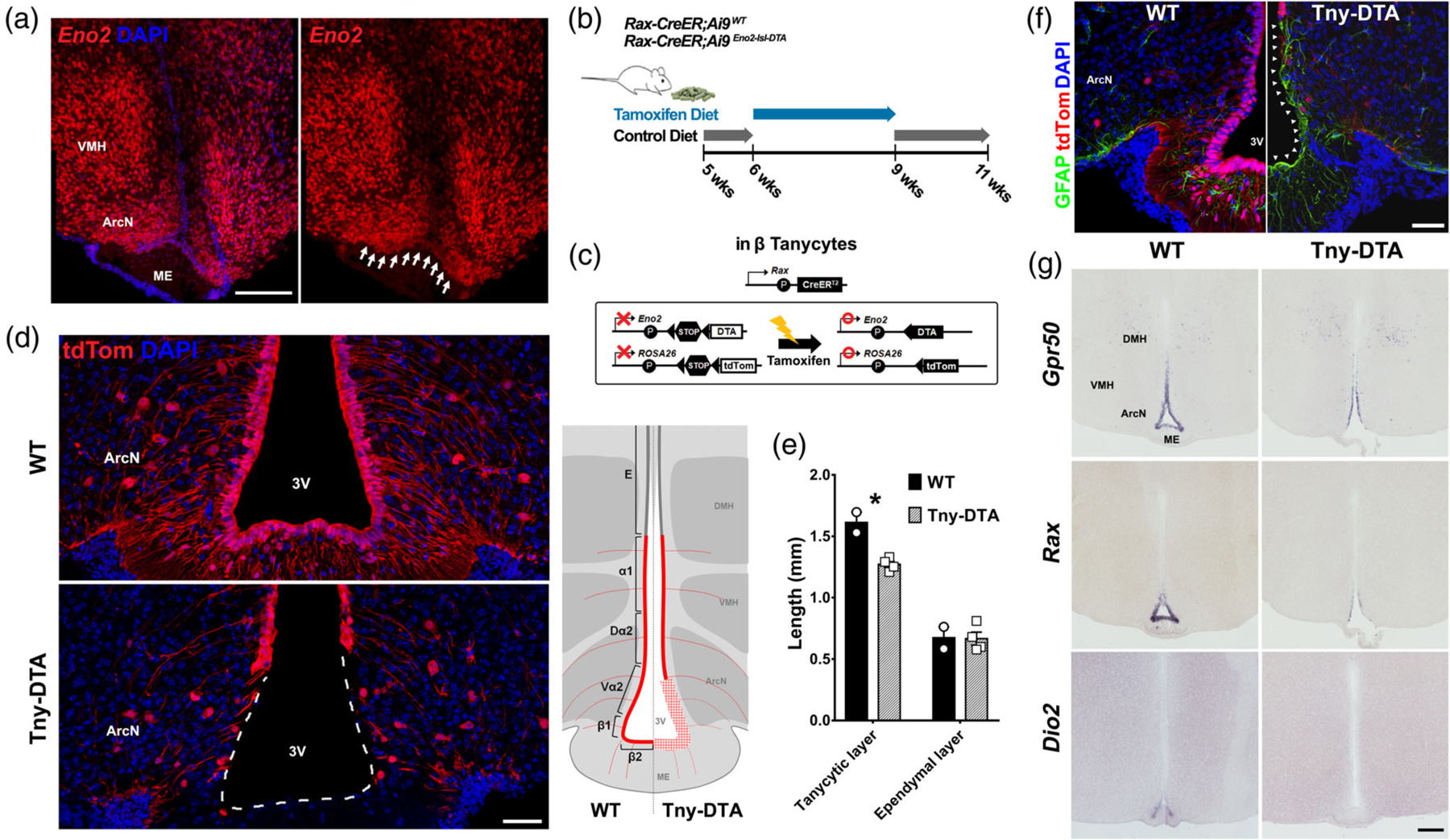
Selective genetic ablation of tanycytes of the ArcN and ME. (a) Eno2 mRNA expression in tanycytes located near the ArcN and ME (white arrows). (b) Schematic diagram showing the time schedule for administration of tamoxifen diet. Five-week-old Rax-CreER;Ai9 (WT) or Rax-CreER;Eno2-lsl-DTA;Ai9 (Tny-DTA) mice were fed with control diet which, aside from lacking tamoxifen, has the same dietary components as the tamoxifen diet, for a week followed by 3 weeks of tamoxifen diet. The mice had 1 week of washout to allow for clearance of tamoxifen before experiments were conducted. (c) Schematic diagram showing the approach used to conditionally ablate tanycytes of the ArcN and ME. By using the Rax-CreER line, Cre recombination induces tdTom expression in all subtypes of tanycyte while DTA expression is specific in Eno2-positive beta-tanycytes and ventral alpha-2 tanycytes. (d) Immunohistochemistry for tdTom showing nearly complete ablation of tanycytes in the ArcN and ME. A diagram inset on the right shows the ablated region (red plaid) lacking tdTom expression in the Tny-DTA mice. E, Ependymal cells; α1,alpha-1 tanycytes; Dα2, dorsal alpha-2 tanycytes; Vα2, ventral alpha-2 tanycytes; β1, beta-1 tanycytes; β2, beta-2 tanycytes. (e) Quantification of reduction of ventricular surface occupied with tdTom-positive tanycytes (tanycytic layer) following tamoxifen-induced ablation as shown in (d). Ependymal cells are indicated as tdTom-negative ventricular cells in the dorsal hypothalamus. (f) Immunohistochemistry for GFAP indicating glial scar formation in the ventricular region following tanycyte ablation (arrowheads). (g) mRNA in situ hybridization using probes for tanycyte marker genes Gpr50, Rax, and Dio2. There is no sex-difference in ablation pattern or scale, and only male data was used that correspond to the male-specific metabolic phenotype which will be shown later. Scale bar: 50 μm (d, f), 200 μm (a, g). *p < .007, two-tailed Student’s t test
