Figure 5. Cdk activity controls the size of HLB.
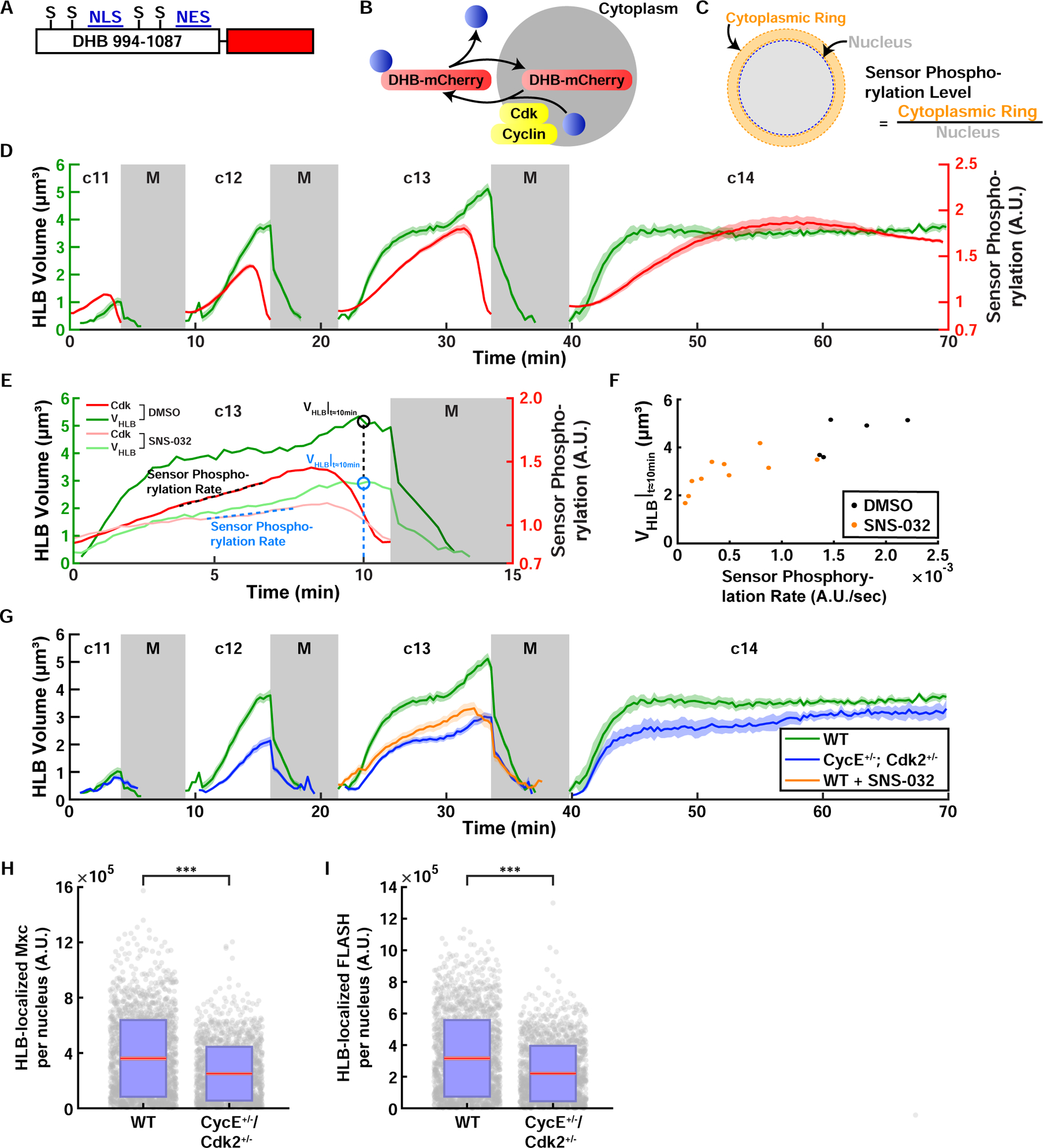
(A) Cdk sensor adapted from Ref (Spencer et al., 2013). Human DNA Helicase B (DHB) amino acids 994–1087 were fused with the fluorescent protein mCherry on the C terminus. S: CDK consensus phosphorylation serine residue, NLS: nuclear localization signal, NES: nuclear export signal. (B) Schematic of Cdk-mediated translocation of the sensor DHB-mCherry. (C) Method used to quantify the sensor phosphorylation level. mCherry fluorescence levels of the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus (cytoplasmic ring) and the nucleus were measured and the sensor phosphorylation level was estimated by calculating the cytoplasmic-to-nuclear mCherry fluorescence ratio. (D) HLB size (green, left axis) and Cdk sensor (red, right axis) dynamics in cycles 11–14. N=10 embryos. (E) Representative quantifications of HLB size in HLB and Cdk sensor dynamics for DMSO control and SNS-032 (Cdk2 inhibitor) injected embryos during cycle 13. VHLB|t≈10min: HLB size 10 minutes after injection. Sensor Phosphorylation Rate, quantified as the slope of the sensor readout. (F) HLB size plotted against sensor phosphorylation rate. VHLB|t≈10min: HLB size 10 minutes after injection. (G) HLB size from embryos laid by WT mothers (green), CycE and Cdk2 double heterozygous mothers (blue), and Cdk2 inhibitor injected embryos (orange). N=10 embryos (WT), 20 embryos (CycE Cdk2 double het), 13 embryos (Cdk2 inhibitor). Total HLB-associated Mxc (H) and FLASH (I) from wild type embryos and embryos laid by CycE+/− , Cdk2+/− heterozygous mothers. Red, 95% confidence interval for the mean. Blue, 1 standard deviation. N=46 embryos, 1997 nuclei (WT); N= 47 embryos, 1692 nuclei (CycE+/− , Cdk2+/−). p<10−4 (two sample t test) for both panels. A.U., arbitrary units. c, cycle. M, mitosis. See also Figure S5 and Videos S4–S5.
