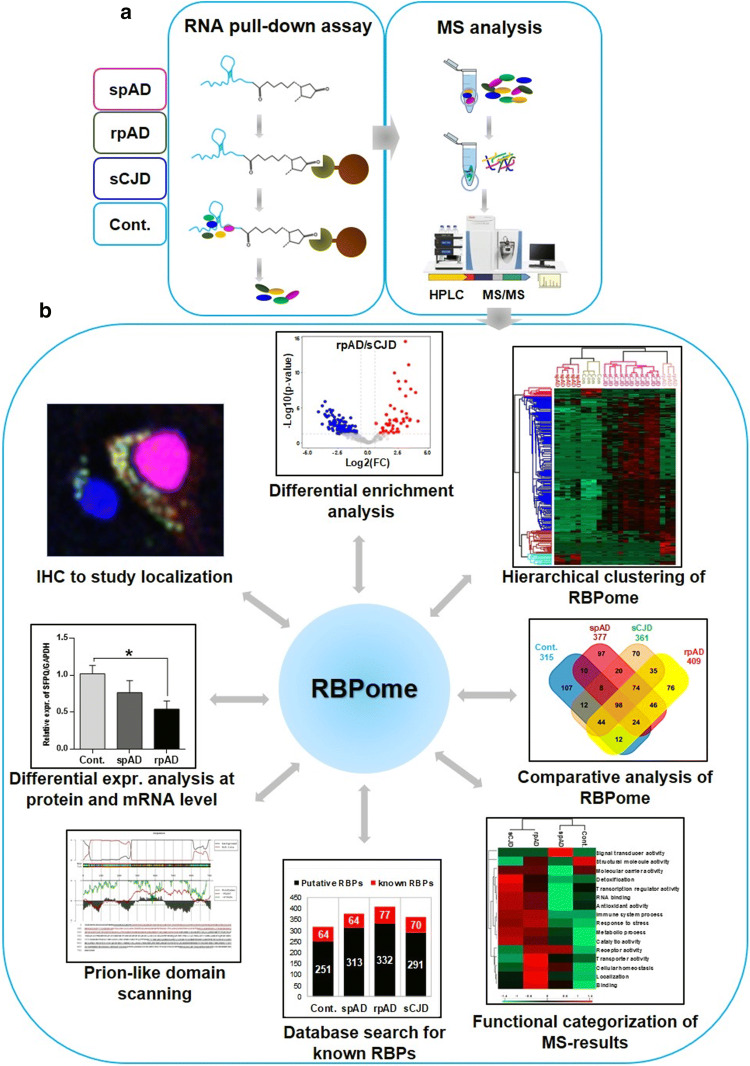
Fig. 1.
Identification of RNA-binding proteins by RNA pull-down assay and mass spectrometry analysis. a Total RNA was isolated from the human brain frontal cortical region of 20 cases (spAD, rpAD, sCJD-MM1, sCJD-VV2 as well as controls). Bead-only control was used for non-specific binding. Isolated protein complexes were identified quantitatively using MS/MS analysis. In total, 1091 proteins were identified and quantified at a minimum peptide count of 2 and a protein threshold of 99%. b Target selection from proteomic investigation and their pathological characterization in the post-mortem human brains: a combination of bioinformatic and computational approaches was used to find out significant hits from the proteomic study, including differential enrichment analysis of MS data, hierarchical clustering analysis to visualize global proteome profile, comparative RBPome analysis, Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment analysis, database search for identification of bona-fide and novel/putative RBP candidates, and prion-like domain scanning with PLAAC database. Target candidates prioritized from proteomic study were pathologically characterized in the post-mortem human brain, using various techniques including immunoblotting, qRT-PCR and immunohistochemical analysis