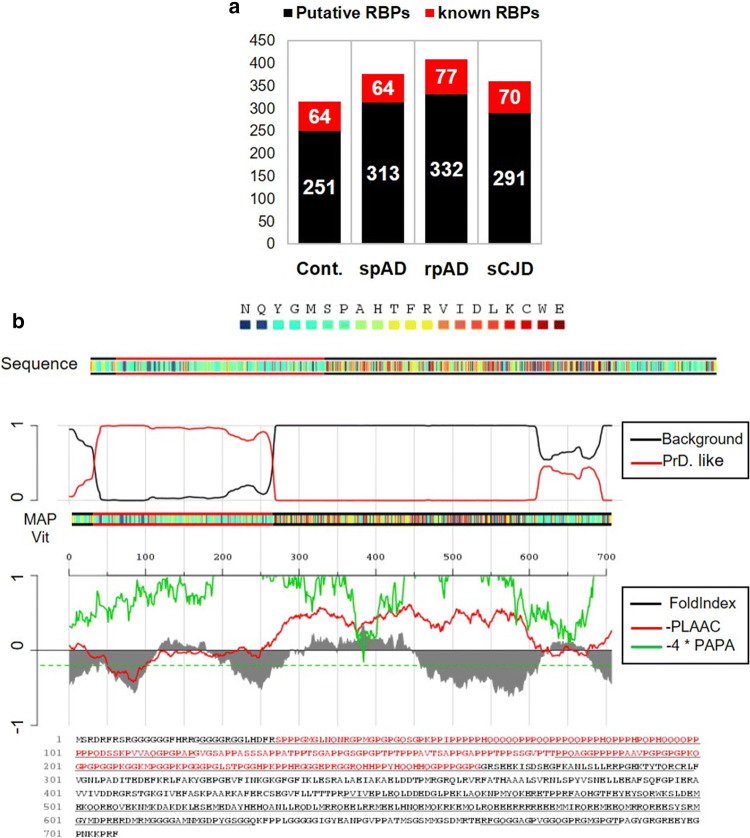
Fig. 4.
Identification of canonical and putative RBP candidates. RNA-binding protein candidates were isolated and identified from the human brain frontal cortical region of 20 cases (spAD, rpAD, sCJD-MM1, sCJD-VV2 as well as controls). a The identified proteomic candidates were searched for RNA-binding annotation in the UniProtKB database. The bar graph is representing two categories. The category I (red) indicates canonical RBPs (known), and category II (black bar) represents potential novel/putative RBP candidates from each group. b Identification of SFPQ-prion-like domain by PLAAC database. The amino acid sequence of SFPQ is represented in colour coded boxes. The red line in the top panel represents the probability of a prion domain against the background. The plots in the middle panel show fold-index scores in grey [60], the log-likelihood (LLR) ratio scores in red [2], and the predicted prion propensity (PPP) in green [81]. Negative scores represent disorder and prion propensity, dashed green line is indicating the cutoff value of PPP > 0.05. The bottom panel is showing the primary sequence of SFPQ with PLD in red colour [2]