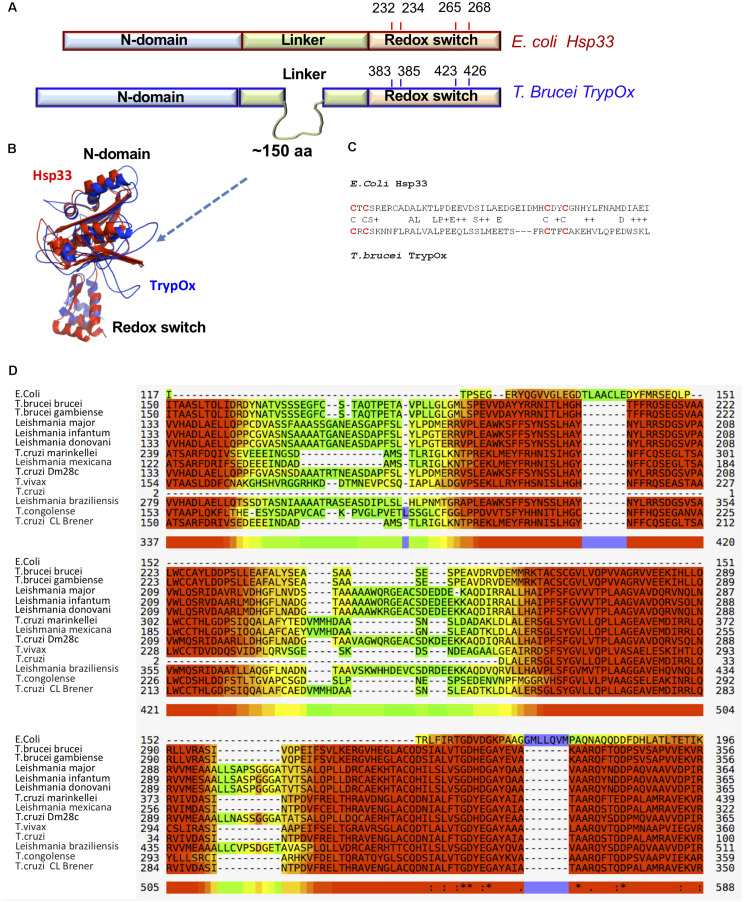
FIGURE 4.
Sequence and structural similarity of TrypOx and E. coli Hsp33. (A) Schematic representation of a sequence alignment between E. coli (red) and T. brucei (blue) orthologs. The alignment points to the extension of the linker domain in the T. brucei ortholog. The position of the conserved cysteines (oxidation of which triggers chaperone activity in bacterial Hsp33) is shown. (B) Structural alignment of the TrypOx model (blue) with reduced B. subtilis Hsp33 (PDB ID:1VZY) shows high conservation of the N-terminal and C-terminal domains. (C) Sequence alignment of the C-terminal redox domain from E. coli and T. brucei orthologs. The redox-sensitive cysteines are in red. (D) Multiple alignment of the unique linker sequence Hsp33 homologs from Trypanosoma and Leishmania species aligned with E. coli Hsp33. The alignment was done by MUSCLE (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/), color code: red to yellow, indicating high to low sequence of conservation.