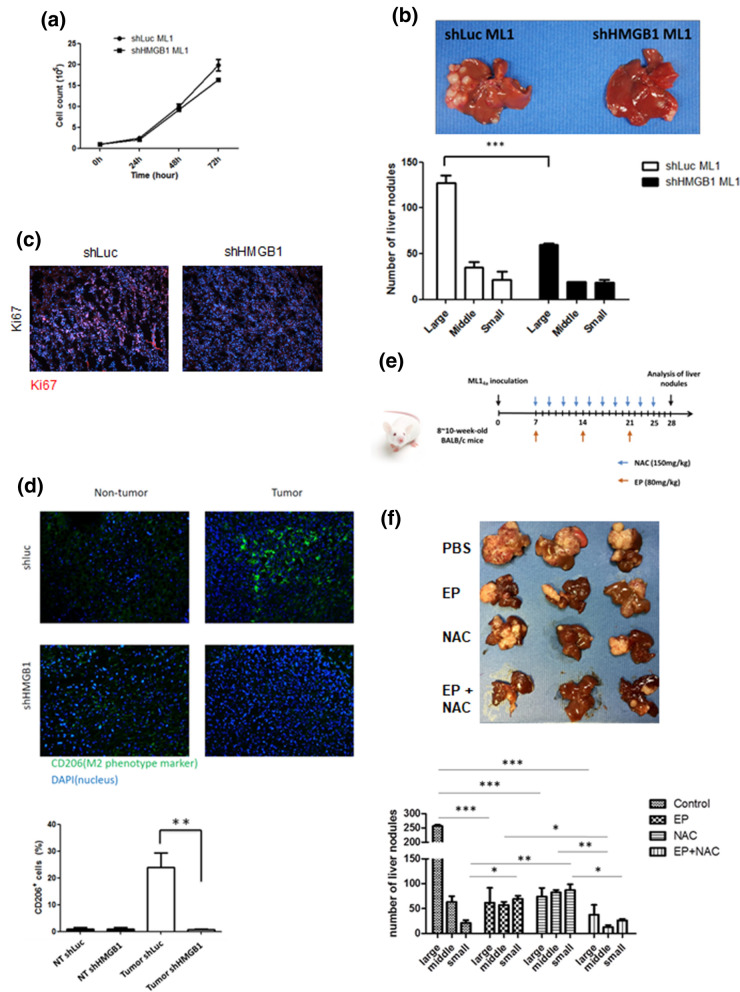
Figure 6.
Blockage of HMGB1 and ROS reduces amounts of tumor-associated M2 macrophages and attenuates hepatoma growth in mice. (a) Cell growth of shLuc and shHMGB1 ML-14a cells was monitored for 72 h. (b,c) BALB/c mice (n = 5) were intrasplenically injected with shLuc or shHMGB1 ML-14a cells. After 28 days post injection, all mice were sacrificed, and their livers were removed to quantify the numbers and sizes of nodules (b). Parts of these livers were also sectioned to stain with Ki67 or anti-CD206 antibodies (c,d). (e,f) Schematic diagram of treatment protocol. 8 to 10 week old BALB/c mice (n = 5) were intrasplenically inoculated with ML-14a cells to establish the liver nodule formation. NAC (150 mg/kg) was given to the mice intraperitoneally at two-day intervals beginning on day 7 post tumor injection. EP (80 mg/kg) was given to mice intraperitoneally at seven-day intervals beginning on day 7 post tumor injection. On day 28 post tumor injection, all treated-mice were sacrificed and their livers were removed to quantify the numbers and sizes of nodules (e). Results were quantified from 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001.