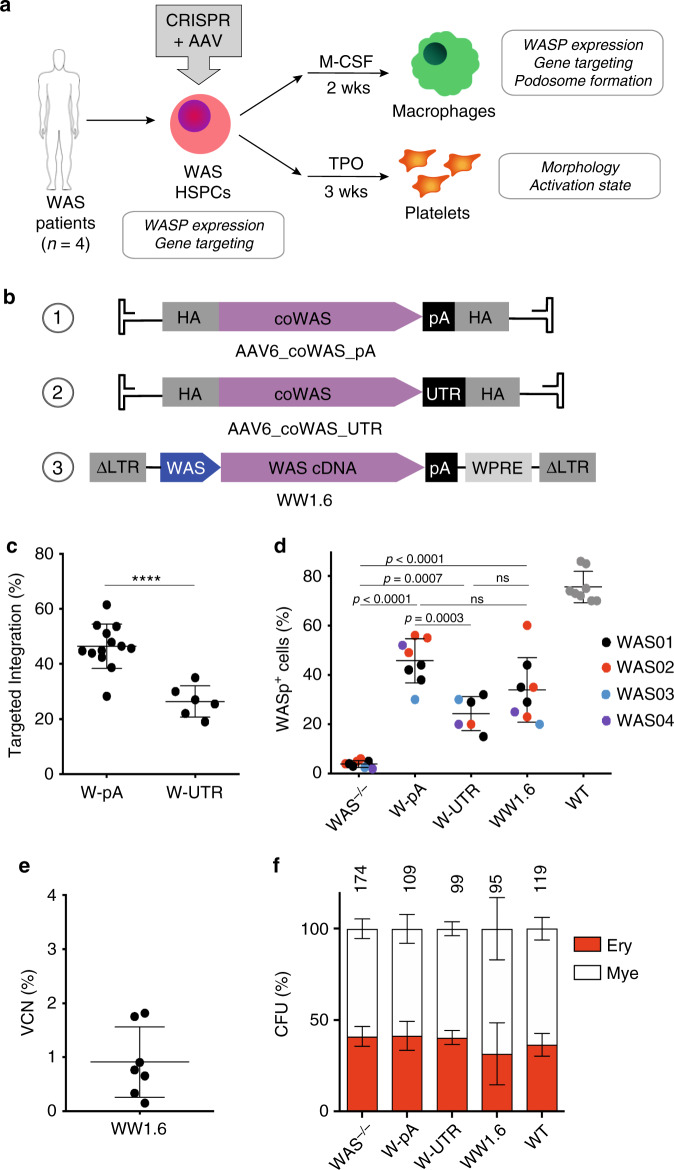
Fig. 2. Gene editing of WAS HSPCs.
a Experimental plan to assess functional correction of the WAS defect in macrophages and platelets by targeting WAS HSPCs. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Atrtribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com. b Schematic of WAS corrective AAV6 donor vectors containing the coWAS cDNA followed by either a BGH polyA signal (coWAS_pA) or WAS 3′UTR (coWAS_UTR). In parallel, the same cells were transduced with a lentiviral vector (WW1.6) currently used in WAS gene therapy clinical trial (HA homology arms, WAS WAS promoter, LTR long terminal repeats, WPRE woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element). c Rates of targeted integration achieved with the two AAV6 donor vectors detected by ddPCR (n = 6 and 13 independent experiments for W-UTR and W-pA, respectively, from 4 different donor sources; Asterisks indicate p-values: ****p < 0.0001, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test). d Quantification of WASp expression in mock, edited, LV-transduced WAS HSPC and healthy HSPCs (WT) by flow cytometry (n = 8 independent experiments for all groups except for W-UTR (n = 6) from four different donor sources; exact p-values are shown in the panel, NS: p > 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). e Quantification of the number of lentiviral vector copies integrated into the genome of transduced WAS HSPCs (VCN, vector copy number; n = 7 experiments from four different donors). f Plots representing the percentage of myeloid (white) and erythroid (red) GFP-positive colonies formed in methylcellulose by mock, edited, transduced WAS HSPCs and healthy HSPCs (WT). Absolute numbers of clones derived from each condition are shown (n = 4 experiments from four different donors; NS: p > 0.05, as analysed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). Data in Fig. 2 are presented as mean ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.