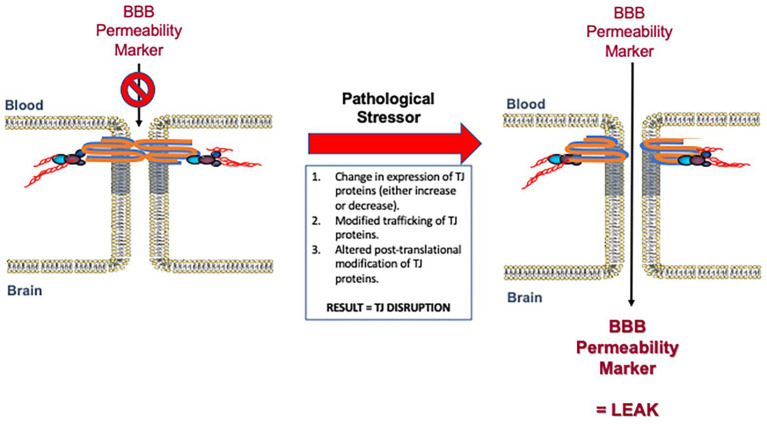
Figure 3.
Disruption of blood-brain barrier (BBB) tight junction protein complexes in response to pathological stressors. Pathophysiological mechanisms can cause measurable changes in tight junction functional integrity by various mechanisms. Such mechanisms include (i) modulation in the expression of tight junction proteins as reflected by either an increase or decrease in specific protein levels; (ii) changes in trafficking of constituent proteins away from the tight junction; and/or (iii) altered post-translational modification of specific tight junction proteins. These mechanisms may occur alone or in combination to enable dynamic remodeling of the tight junction in the setting of disease. Changes in the molecular composition of tight junction protein complexes results in increased paracellular permeability (i.e., leak) to specific BBB permeability markers described in Table 1. Modified with permission from Abdullahi et al. (2018).