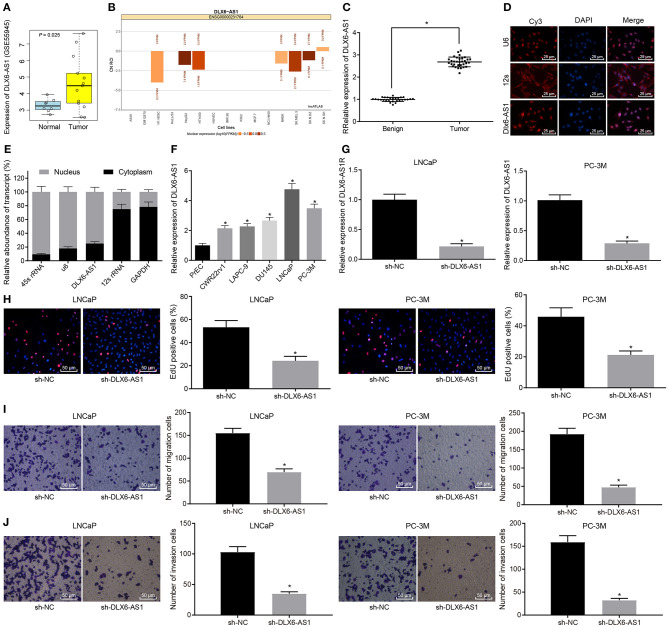
Figure 1.
LncRNA DLX6-AS1 is highly expressed in prostate cancer and silencing DLX6-AS1 inhibits their proliferation, migration and invasion. (A) DLX6-AS1 expression in prostate cancer tissues and normal tissues in the microarray dataset GSE55945; (B) prediction of subcellular localization of DLX6-AS1 expression in prostate cancer cells by the lncATLAs website; (C) DLX6-AS1 expression in benign prostatic hyperplasia tissues (n = 28) and cancer tissues (n = 32) measured by RT-qPCR; (D) localization of DLX6-AS1 in prostate cancer cells detected by FISH assay (× 400); (E) localization of DLX6-AS1 in prostate cancer cells identified by subcellular fractionation assay; (F) DLX6-AS1 expression in prostate cancer cells measured by RT-qPCR; (G) DLX6-AS1 expression assessed by RT-qPCR after sh-DLX6-AS1 transduction in LNCaP and PC-3M cell lines; (H) the images of EdU-positive cells and quantitation of cell count detected by EdU staining (× 200) after sh-DLX6-AS1 transduction in LNCaP and PC-3M cell lines; (I) the migration ability of cells and the number of migrating cells measured by Transwell assay (× 200) after sh-DLX6-AS1 transduction in LNCaP and PC-3M cell lines; (J) the invasion ability of cells and the number of invasion cells measured by Transwell assay (× 200) after sh-DLX6-AS1 transduction in LNCaP and PC-3M cell lines. *p < 0.05. Measurement data were summarized as mean ± standard deviation. Paired data between two groups were compared using paired t-test and unpaired data using unpaired t-test. Comparisons among multiple groups were conducted by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. Cell experiment was repeated three times.