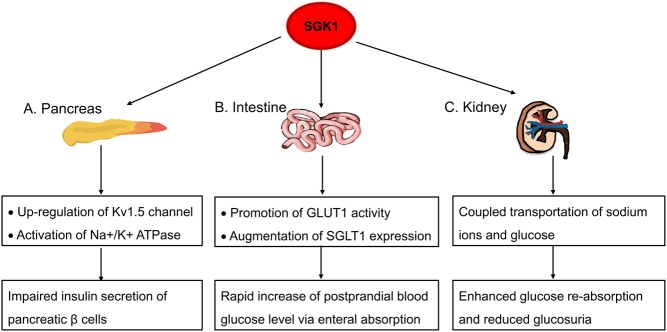
Figure 2.
SGK1 exacerbates hyperglycemia by acting on pancreas, intestine and kidney. (A) In pancreas, SGK1 abnormally activates Kv1.5 channel and Na+/K+ ATPase to interfere with the membrane polarization and repolarization process. As a result, the insulin-secreting activity of pancreatic β cell is severely impaired. (B) In intestine, SGK1 promotes the activity of GLUT1 and SGLT1, causing a rapid increase of postprandial blood glucose level via enteral absorption. (C) In kidney, SGK1 facilitates coupled transportation of sodium ions and glucose, which enhances glucose reabsorption and reduces glucosuria.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a