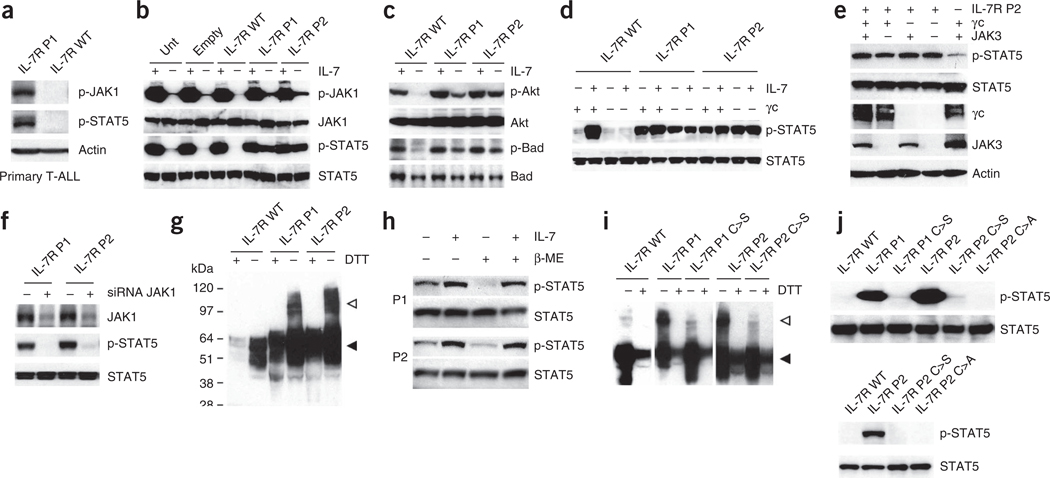
Figure 3.
IL7R mutations induce constitutive signaling in a manner that is independent of IL-7, γc and JAK3 and relies on disulfide bond promotion of homodimer formation. (a) We analyzed primary T-ALL cells collected at diagnosis from cases with mutant (P1) and wild-type IL7R by immunoblot for JAK1 and STAT5 phosphorylation. (b,c) We cultured D1 cells expressing human wild-type or mutant (P1 and P2) IL-7Rα without IL-7 for 4 h, stimulated them or not with IL-7 for 20 min and evaluated them for activation of JAK-STAT (b) and PI3K-Akt (c) pathway activation by immunoblot. (d) We analyzed 293T cells reconstituted with JAK3, STAT5 and wild-type or mutant IL-7Rα, and expressing or not expressing γc, for constitutive and IL-7–induced (15 min stimulation) STAT5 phosphorylation. (e) We transfected 293T cells with IL-7Rα P2 and the remaining components of the IL-7R signaling machinery as indicated and evaluated them for STAT5 phosphorylation. (f) We transfected 293T cells with IL-7Rα P1 or P2 and small interfering RNA (siRNA) against JAK1 (+) or control non-targeting siRNA (−) and evaluated them after 36 h for JAK1 expression and STAT5 phosphorylation. (g) Lysates from D1 cells expressing wild-type or mutant IL-7Rα were treated or untreated with the reducing agent DTT and analyzed for IL-7Rα expression by immunoblot. The monomeric and dimeric forms of the receptor are denoted by black and white arrowheads, respectively. (h) We pretreated 293T cells expressing IL-7Rα P1 and P2 and the remaining components of the IL-7R signaling machinery with β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME), stimulated or unstimulated them with IL-7 for 15 min and subsequently evaluated them for STAT5 phosphorylation by immunoblot. (i) We analyzed the D1 cells expressing each of the indicated IL-7R constructs for IL-7Rα expression by immunoblot. (j) We assessed the signaling elicited by each indicated mutant form expressed in D1 (top) or 293T (bottom) cells by detection of STAT5 phosphorylation.