Figure 1.
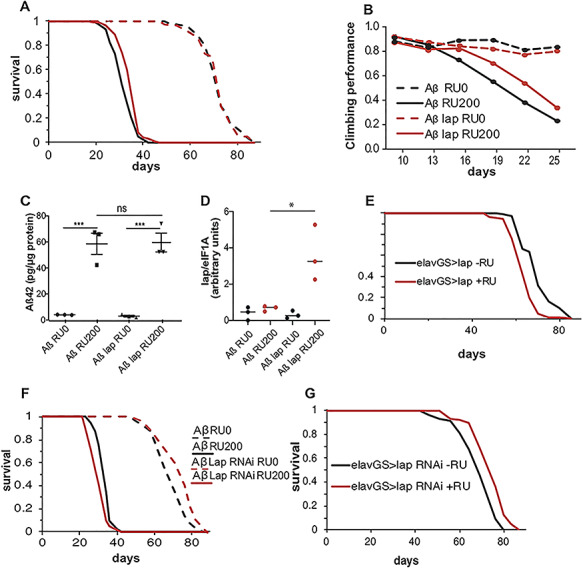
lap alleviates Aβ42 toxicity. (A) Survival curves of flies expressing Aβ, with (red lines, UAS-Aβ/UAS-lap; elavGS/+) and without (black lines, UAS-Aβ/+; elavGS/+) lap co-overexpression, in adult neurons (RU200, solid lines) and uninduced controls (RU0, dashed lines). Expression of Aβ in neurons shortened lifespan, and lap co-overexpression significantly improved this shortened lifespan. n > 120 per condition. Aβ RU0 versus Aβ RU200, P = 1.1E−72; Aβ RU0 versus Aβ lap RU0, ns, not significant; Aβ lap RU0 versus Aβ lap RU200, P = 2.44E−47; Aβ RU200 versus Aβ lap RU200, P = 1.8E−5, determined by log–rank test. There was a significant interaction of genotype and RU by Cox proportional hazard analysis, P = 0.016, indicating that expression of lap significantly extended the lifespan of Aß-expressing flies. (B) Locomotor performance index of flies of the same genotypes as in (A). Aβ caused a climbing defect, which was significantly improved by the co-overexpression of lap, n = ~50 flies per condition. There was a statistically significant interaction between RU and genotype by ordinal logistics, P = 0.00040826, indicating that the expression of lap significantly improved the climbing of Aß-expressing flies. (C) Aβ42 protein levels, measured by ELISA, in the heads of 21-day-old flies expressing Aβ with or without co-overexpression of lap in neurons (RU200) and uninduced controls (RU0). lap co-overexpression had no effect on Aβ42 levels. Means ± SEM, n = 3 biological replicates of 10 heads per replicate per condition. F(3,8) = 34.53, P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA;***P < 0.01, ns, not significant, comparison by Tukey’s post hoc test. (D) qPCR of lap mRNA levels in fly heads expressing Aß, Aß and lap (RU200) and their uninduced controls (RU0), showing overexpression of lap in the Aß, lap expressing flies (F(3,8) = 1.987) by one-way ANOVA *P = 0.0088 for comparison between the two induced conditions. (E) Adult survival curves of lap overexpression in adult neurons (RU200, red line) and uninduced controls (RU0, black line), n > 120 per condition, P = 4.5E−16, by log–rank test. (F) Adult survival of flies harbouring Aβ with (red lines, UAS-Aβ/+; elavGS/UAS-lap-RNAi) or without (black lines, UAS-Aβ/+; elavGS/+) lap RNAi in adult neurons (RU200, solid lines) and uninduced controls (RU0, dashed lines). Inhibition of lap reduces longevity of Aβ-expressing flies. n > 120 per condition. Aβ RU0 versus Aβ RU200, P = 7.6254E−72; Aβ RU0 versus Aβ lap RU0, P = 1.48871E−06; Aβ lap RU0 versus Aβ lap RU200, P = 1.65991E−69; Aβ RU200 versus Aβ lap RU200, P = 3.2225E−10, by log–rank test. There was a significant interaction of genotype and RU by Cox proportional hazard analysis, P = 9.5E−06, indicating that downregulation of lap significantly shortened the lifespan of Aß-expressing flies. (G) Adult survival curves of lap RNAi flies in adult neurons (RU200, red line) and uninduced controls (RU0, black line), n > 120 per condition. P = 1.08638E−09, by log–rank test.
