Figure 4.
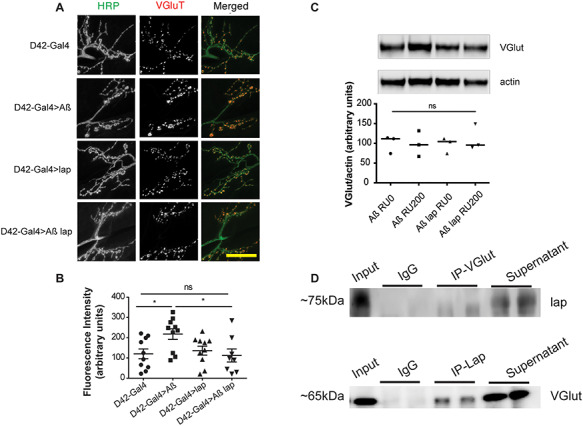
Lap reduces the Aβ-induced accumulation of VGlut at the larval NMJ. (A) Confocal images of the NMJs of wandering third-instar larvae expressing the D42-Gal4 driver alone (+/+; D42-Gal4/+), and Aβ (UAS-Aβ/+; D42-Gal4/+), lap (UAS-lap/+; D42-Gal4/+), or Aβ + lap (UAS-Aβ/UAS-lap; D42-Gal4/+) driven by D42-Gal4. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Fluorescence intensity scores are plotted as means ± SEM, n > 7 per condition. F(3,34) = 3.576, P = 0.0238 determined by one-way ANOVA; *P < 0.05, ns, not significant, comparison by Tukey’s post hoc test. (C) Western blot and quantification of VGlut relative to actin in adult Drosophila heads expressing Aß or Aß and lap (RU200) and their uninduced controls (RU 0). Genotypes: UAS-Aβ; elavGS/+, UAS-Aβ/UAS-lap; elavGS/+. (D) Western blots of fractions of a co-IP for VGlut (upper) and lap (lower) from the heads of wild-type adult flies, probed for lap (upper) and VGlut (lower). Samples are head extracts before the IP was started (input), bead-only pull-down (IgG) showing no non-specific binding; pull-down with the indicated antibody (IP-VGlut, IP-lap), showing successful pull-down of the binding partner; supernatant after the pull-down (supernatant), showing only partial depletion; please see Materials and Methods for details. These IP show that VGlut can pull-down lap and lap can pull-down VGlut. All co-IPs were run in duplicate.
