Figure 2.
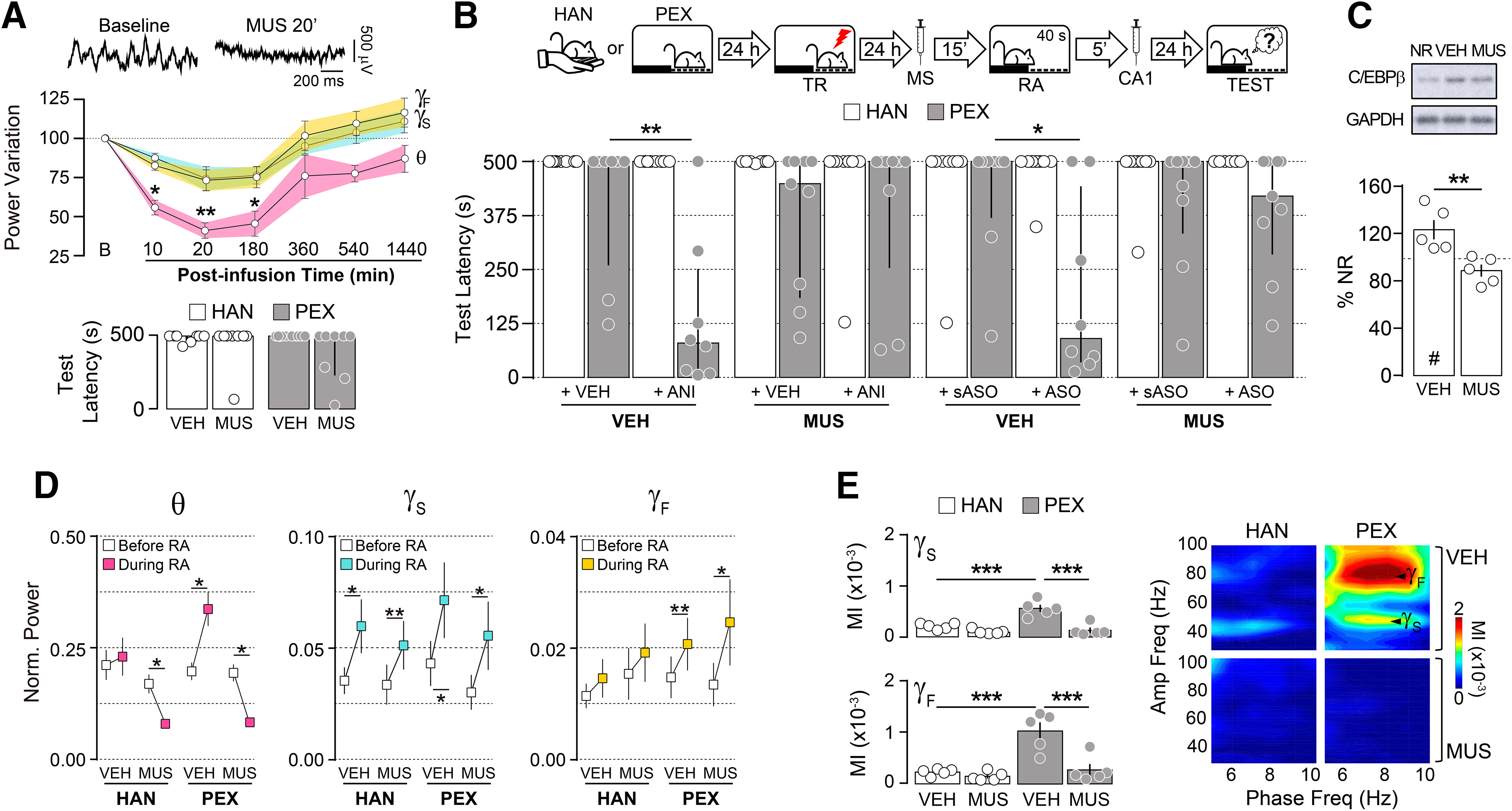
Medial septum inactivation during avoidance memory reactivation impedes hippocampal theta-gamma phase-amplitude coupling and memory destabilization. A, Top, Representative raw hippocampal LFP traces at baseline and 20 min postinfusion from animals given MUS (0.2 µg/µl) into the MS. Middle, Theta (θ; 5–10 Hz), Sgamma (γS; 35–55 Hz), and Fgamma (γF; 65–100 Hz) power variation from baseline (B) at different time points after intra-MS MUS infusion (n = 4). Bottom, Rats were handled (HAN animals) or allowed to freely explore the SDIA training box (PEX animals) during 5 min once daily for 5 consecutive days. Twenty-four hours after the last handling or pre-exposition session, animals were trained in SDIA(0.8 mA/2 s). One day later, they received injections of VEH (0.9% saline) or MUS into MS, and 15 min thereafter were submitted to a retention test session (n = 8/group). B, One day after training, HAN and PEX animals received VEH or MUS into MS, and 15 min thereafter were submitted to a 40-s-long nonreinforced memory RA session. Five minutes after RA, the animals received bilateral intradorsal CA1 infusions of VEH, ANI (160 µg/side), C/EBPβ-ASO (2 nmol/µl), or sASO (2 nmol/µl). Retention was evaluated 1 d later (TEST; n = 8–9/group). C, PEX animals were treated as in B, but 90 min after RA were killed by decapitation, and the dorsal CA1 region dissected out and homogenized to determine C/EBPβ and GAPDH protein levels by immunoblotting (n = 5/group). D, Normalized theta (θ), Sgamma (γS), and Fgamma (γF) power before and during RA for HAN and PEX animals that received intra-MS VEH or MUS 15 min before RA (n = 5/group). E, Mean theta-Sgamma and theta-Fgamma MI and representative phase-amplitude comodulograms for HAN and PEX animals during RA. Data are expressed as the median ± IQR or mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, #p < 0.05 in one-sample Student's t test with a theoretical mean = 100.
