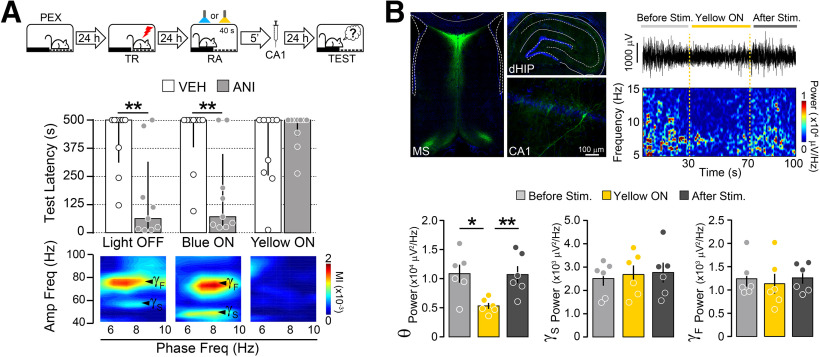
Figure 3.
Medial septum optogenetic silencing impedes memory destabilization. A, Top, Rats expressing archaerhodopsin T in the MS were allowed to freely explore the SDIA training box during 5 min once daily for 5 consecutive days (PEX animals) and 24 h after the last pre-exposition session were trained in SDIA (TR; 0.8 mA/2 s). One day post-TR, animals were submitted to a 40-s-long nonreinforced memory RA session during which the MS was not stimulated (Light OFF) or optogenetically stimulated with blue light (470 nm; Blue ON) or yellow light (565 nm; Yellow ON). 5 min after RA, rats received bilateral injections of VEH (0.9% saline) or ANI (160 µg/side) in dorsal CA1. Retention was evaluated 1 d later (TEST; n = 9–10/group). Bottom, Representative phase-amplitude comodulograms during RA for each experimental group. B, Left top, Representative images showing archaerhodopsin T expression in MS and dorsal hippocampus reported by GFP. Right top, Representative raw hippocampal LFP trace and spectrogram plot showing the effect of MS yellow light stimulation on theta power. Bottom, Bars show mean hippocampal theta (θ; 5–10 Hz), Sgamma (γS; 35–55 Hz), and Fgamma (γF; 65–100 Hz) power before, during, and after light delivery to the MS (n = 6/group). Data are expressed as the median ± IQR or mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.