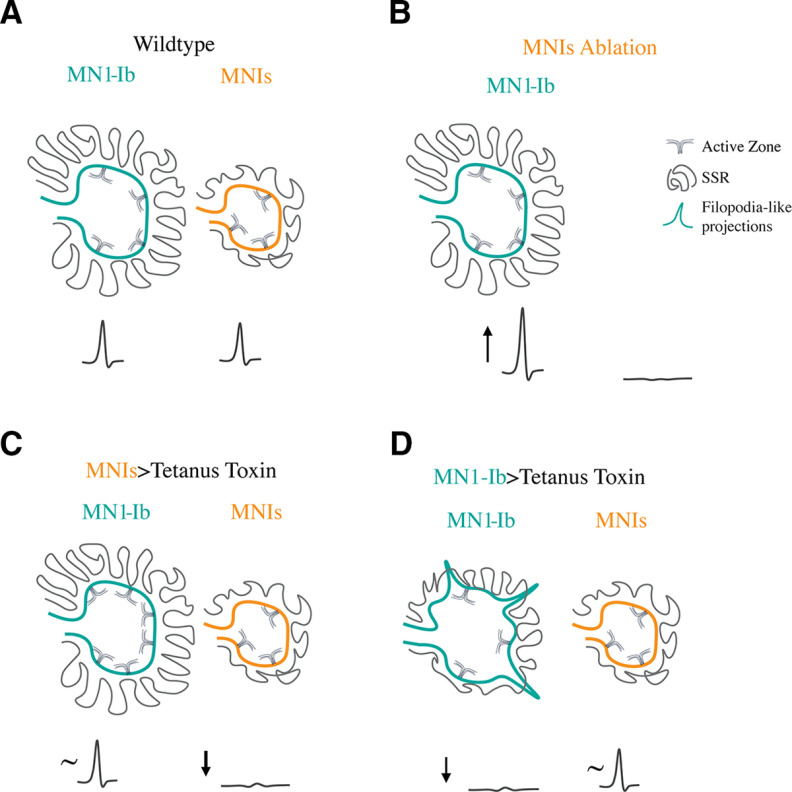
Figure 14.
Summary of observed MN1-Ib plasticity. A, In wild-type, MN1-Ib and MNIs provide similar drive to muscle M1. MN1-Ib forms more synaptic boutons and AZs onto M1 compared with MNIs. B, Ablation of MNIs results in increased output from MN1-Ib, as evidenced by larger EJPs, but does not trigger increases in bouton or AZ number. C, Silencing of MNIs with tetanus toxin triggers increased bouton and AZ number in the coinnervating MN1-Ib. These changes do not increase presynaptic output from MN1-Ib, with EJP amplitude (∼) at M1 unchanged compared with controls. No structural changes are observed in the silenced MNIs. D, Silencing of MN1-Ib with tetanus toxin results in decreased bouton and AZ number at MN1-Ib terminals. Postsynaptic SSR development is also reduced. Presynaptic filopodia-like projections normally restricted to early first instar stage are observed at mature MN1-Ib silenced terminals. No structural or functional (∼) changes occur in the coinnervating MNIs.