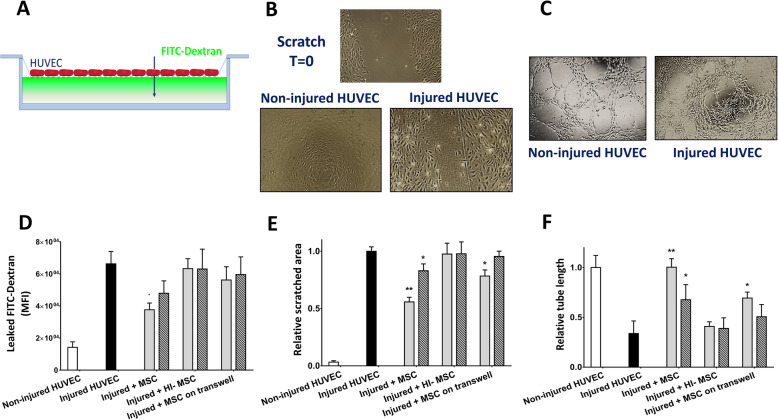
Fig. 4.
MSC repair wound healing capacity, barrier function, and angiogenic properties of injured HUVEC. a HUVEC monolayer permeability was increased after injury. MSC at a 1:2 ratio reduced HUVEC monolayer permeability by 44% after 24 h of incubation. Incubation with HI-MSC or MSC through a transwell had no effect. b Hypoxia-reoxygenation injury decreased the wound healing capacity of HUVEC measured by a scratch assay. After 24 h incubation with MSC at a 1:2 ratio, MSC improved HUVEC capacity to close a scratched area by 45%. Secreted molecules by MSC during incubation through a transwell improved injured HUVEC wound healing by 22%. At a ratio of 1:10 MSC-HUVEC, wound healing capacity was improved by 17% by MSC. HI-MSC had no effect at any ratio. c The total length of tube-like structures formed by HUVEC was measured to quantify angiogenic capacity. Hypoxia and reoxygenation injury decreased HUVEC angiogenic potential by half. After 24 h of incubation with MSC at a 1:2 ratio, injured HUVEC fully recovered their angiogenic capacity. At a 1:10 ratio, MSC improved angiogenic potential of injured HUVEC by 50%. Secreted molecules by MSC at a 1:2 ratio led to a 48% recovery on injured HUVEC angiogenic potential. HI-MSC had no effect at any ratio. d Schematic depiction of endothelial monolayer integrity. Added FITC-conjugated dextran leaks through an injured endothelial monolayer. e Visual representation of non-injured (left) and injured (right) HUVEC angiogenic potential. f Visual representation of HUVEC wound healing capacity. Top panel: a scratch is made to the endothelial monolayer at time point 0 h. Bottom left panel: non-injured HUVEC completely close the scratch after 6 h. Bottom right panel: injured HUVEC are not able to completely close the scratch after 6 h (n = 5). Results are shown as mean ± SD. Significance of the comparison between injured HUVEC and the effect of MSC is shown as **p value < 0.01 and *p value < 0.05