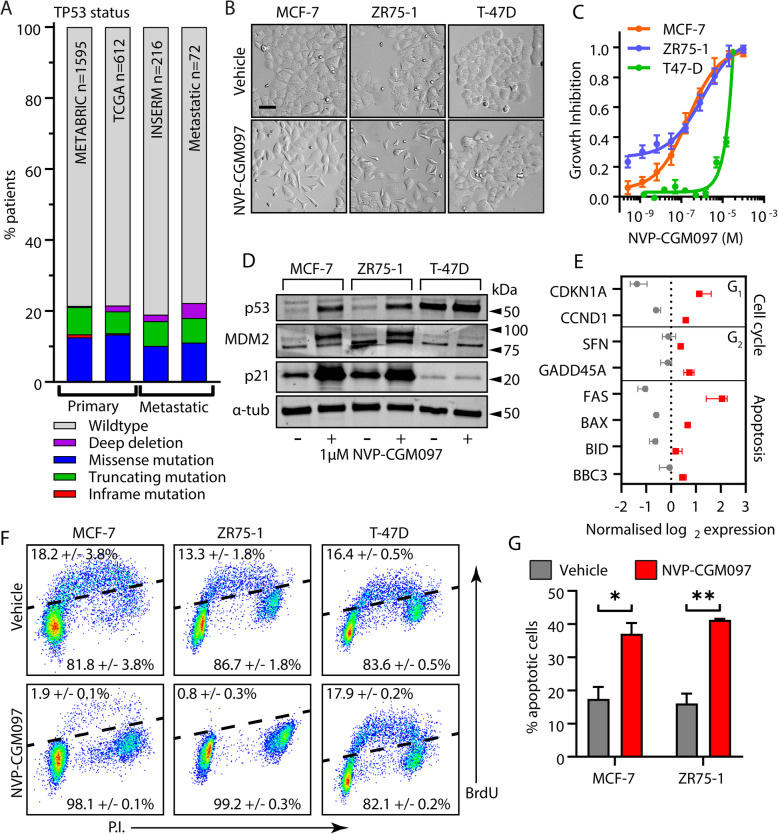
Fig. 1.
MDM2 inhibition reduces viability in a p53 dependent manner in cell line models of ER+ breast cancer. a The frequency of p53 mutation (putative drivers) in ER-positive primary breast cancers – Breast Cancer (METABRIC, Nature 2012 & Nat Commun 2016), Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA, Cell 2015) – and metastatic tumours – The Metastatic Breast Cancer Project (Provisional, October 2018) and Metastatic Breast Cancer (INSERM, PLoS Med 2016) – across public datasets in https://www.cbioportal.org/. b Representative images of MCF-7, ZR75-1 and T-47D cell cultures after exposure to vehicle (0.01% DMSO) or 1 μM NVP-CGM097 for 48 h. Bar = 20 μm. c Growth inhibition relative to vehicle after 48 h treatment with escalating doses of NVP-CGM097 in p53wt MCF-7 (orange) and ZR75-1 (blue), and p53mut T-47D cells (green). d Western blot analysis of p53 and the known p53 transcriptional targets MDM2 and p21 after 48 h incubation with 1 μM NVP-CGM097. α-tubulin staining is shown as an indication of relative loading. See Fig. S1A for full gel and blot images. e Normalised expression of cell cycle regulators and apoptosis markers after treatment with vehicle (0.01% DMSO, grey) or 1 μM NVP-CGM097 (red) for 48 h in MCF-7 cell lines. f Flow cytometry analysis of the incorporation of BrdU over a 2-h period in MCF-7, ZR75-1 and T-47D following a 48 h incubation with 1 μM NVP-CGM097. g Proportion of MCF-7 and ZR75-1 cells staining positive for AnnexinV after treatment for 48 h with vehicle (grey) or 1 μM NVP-CGM097 (red). Statistical significance from Tukey’s multiple comparison test is indicated above each column