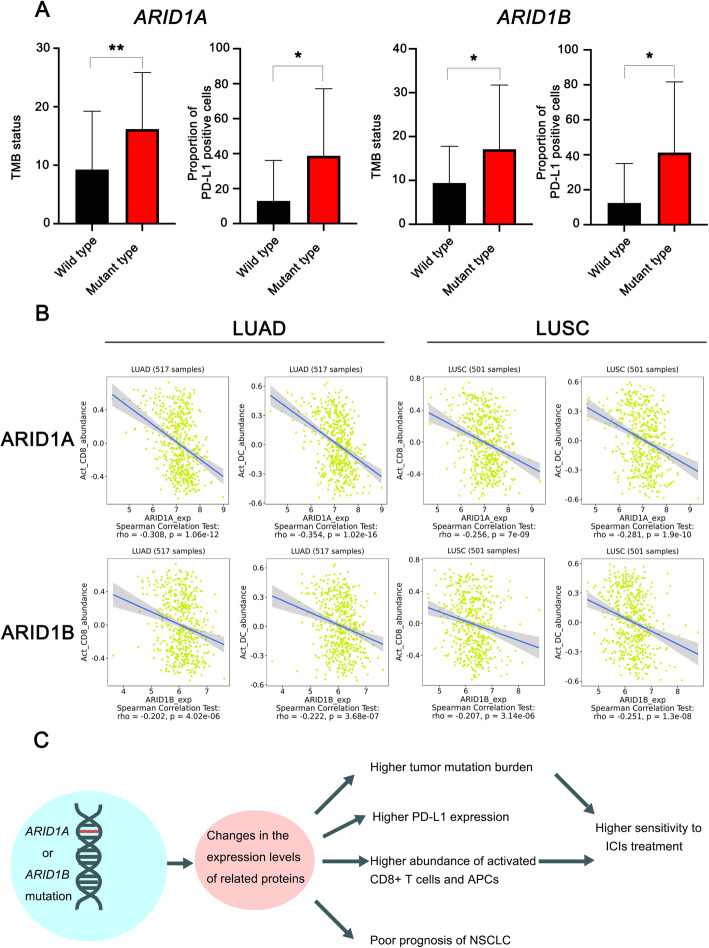
Fig. 4.
ARID1A or ARID1B mutations are tightly associated with sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). a. The comparison of tumor mutational burden (TMB) values and PD-L1 expression grouped by the genomic signatures of ARID1 subunits; b. The correlations between ARID1A or ARID1B expression and the abundances of activated CD8+ T cells and activated dendritic cells (DC) in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC); c. The underlying relationships between prognosis and ARID1A or ARID1B mutation deduced from this research. (**: P<0.01; *: P<0.05)