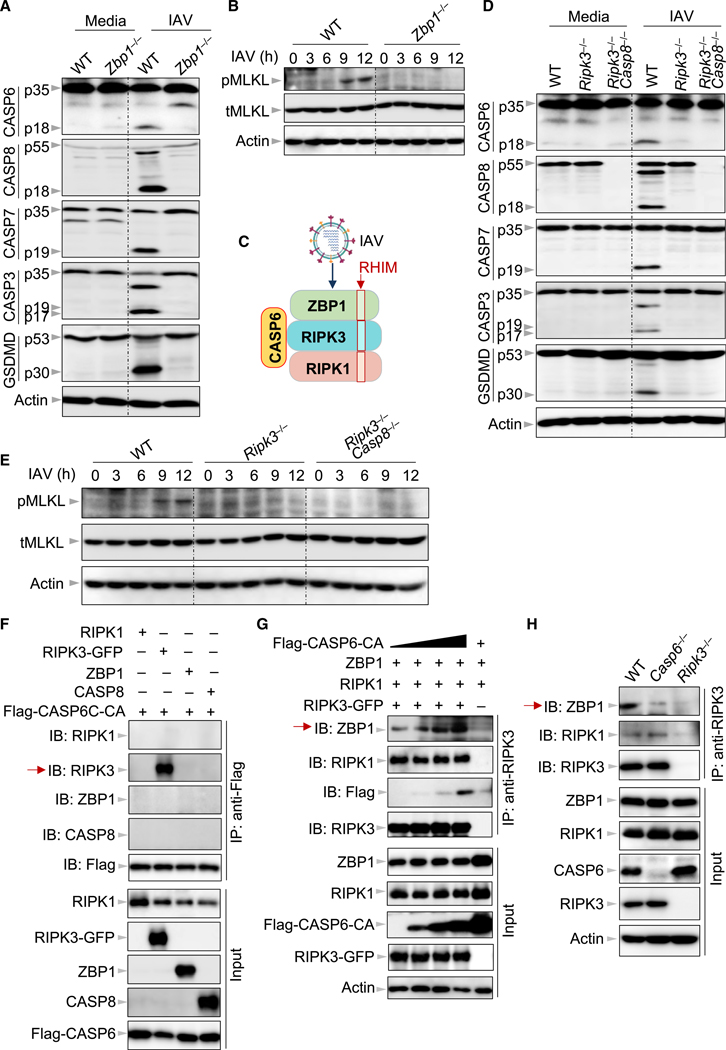
Figure 5. Caspase-6 Is Critical for Enhancing the Interaction between RIPK3 and ZBP1.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of pro- and cleaved forms of caspase-6 (CASP6), −8 (CASP8), −7 (CASP7), −3 (CASP3), and gasdermin D (GSDMD) in bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) after influenza A virus (IAV) infection for 12 h. Actin is used as the internal control.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like (pMLKL) and total MLKL (tMLKL) in BMDMs after IAV infection at the indicated time points. Actin is used as the internal control.
(C) Schematic depiction of the relationship between receptor-interacting protein homotypic interaction motif (RHIM) domain-containing proteins in the Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1)-initiated cell death complex and caspase-6 after IAV infection. The red boxes indicate the RHIM domains.
(D) Immunoblot analysis of pro- and cleaved forms of CASP6, CASP8, CASP7, CASP3, and GSDMD in BMDMs after IAV infection for 9 h. Actin is used as the internal control.
(E) Immunoblot analysis of pMLKL and tMLKL in BMDMs after IAV infection at the indicated time points. Actin is used as the internal control.
(F) Immunoprecipitates and total lysates from 293T cells after co-transfection of FLAG-CASP6 with receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK) 1, RIPK3-GFP, ZBP1, or CASP8 for 30 h.
(G) Immunoprecipitates and total lysates from 293T cells after co-transfection with RIPK1, RIPK3-GFP, and ZBP1 in the absence or presence of FLAG-CASP6 for 30 h.
(H) Immunoprecipitates and total lysates from BMDMs with IAV infection for 16 h. Data are representative of three independent experiments. See also Figures S3, S4, and S5.