Figure 7. MIC26 and MIC27 maintain cardiolipin levels that are required for stability of respiratory chain (super) complexes.
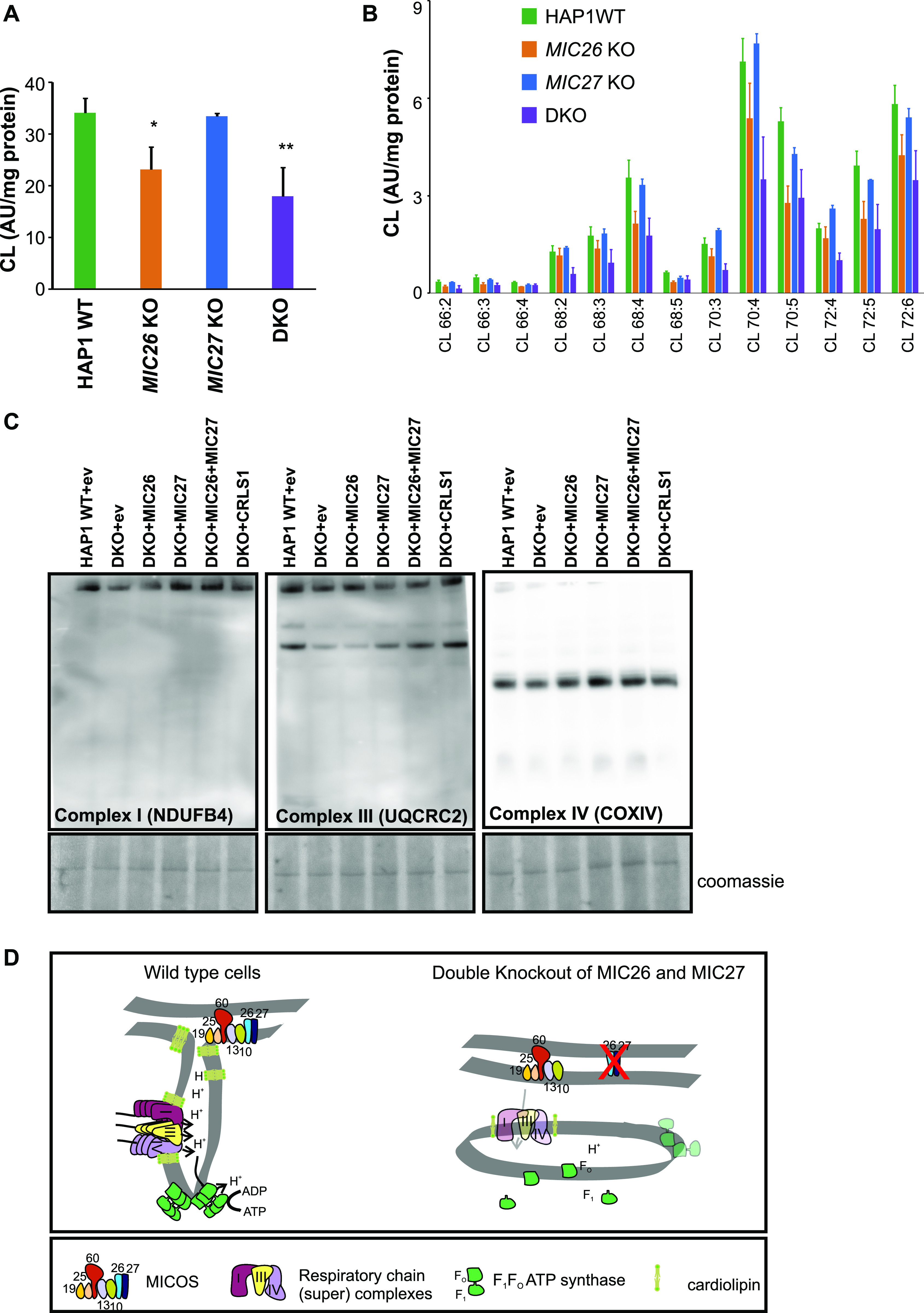
(A) Graph representing the levels of cardiolipin shown as arbitrary units normalized to mg of protein in each cell types show significant reduction in MIC26 KO and double knockout (DKO) cells. *P-value ≤ 0.05, **P-value ≤ 0.01. t test was used for statistical analysis. (B) Graph showing the distribution of various cardiolipin species (arbitrary units normalized to mg of protein) in HAP1 WT, MIC26 KO, MIC27 KO, and DKO cells. (C) Blue-native gel electrophoresis for isolated mitochondria from HAP1 WT expressing empty vector (ev) and DKO cell lines that are stably expressing ev or MIC26 or MIC27 or MIC26 and MIC27 together or CRLS1 (cardiolipin synthase) were solubilized and blotted for antibodies specific for complex I (NDUFB4), complex III (UQCRC2), or complex IV (COX1V). The restoration of staining of respiratory chain (super) complexes compared with DKO (with ev) was found upon expression of MIC26 and MIC27 as well as CRLS1 in DKO cell lines. The part of the BN–PAGE stained with Coomassie is shown to represent the loading among the cell lines. (D) The scheme summarizing the phenotype occurring due to loss of MIC26 and MIC27 that show MIC26 and MIC27 are cooperatively required for the formation of crista junctions, maintenance of cardiolipin levels, and stability of respiratory chain (super) complexes and F1FO–ATP synthase. In addition, MIC26 and MIC27 are required for the assembly of F1Fo–ATP synthase by facilitating the association of F1 and Fo part. Loss of MIC26 and MIC27 leads to impaired respiration.
