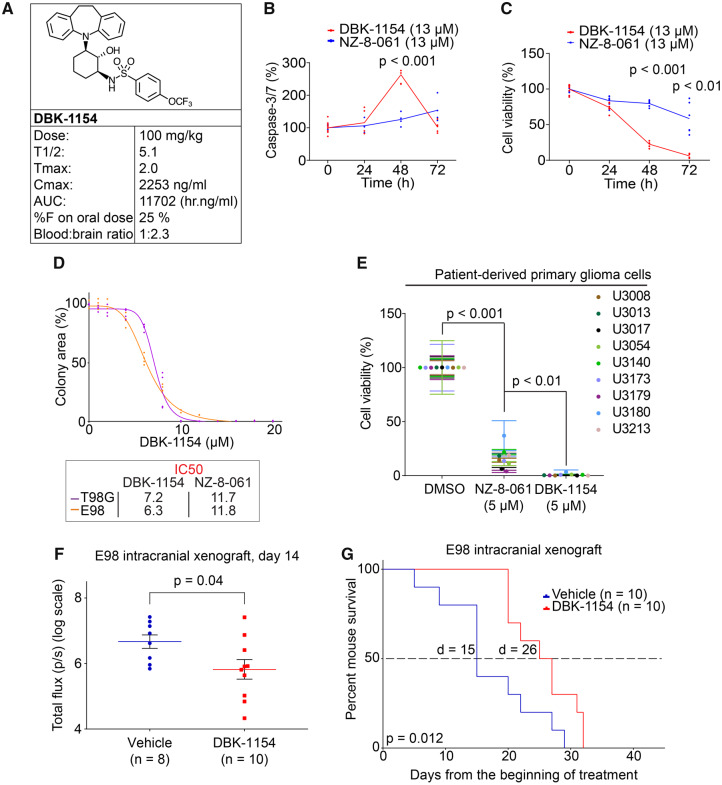
Figure 4.
Oral dosing of DBK-1154 increases survival of mouse with intracranial infiltrative GB xenograft. (A) Mouse in vivo pharmacokinetic parameters (T½ h, Tmax h, Cmax ng/ml, area under curve h.ng/ml, CL ml/h/kg, %F and blood–brain ratio) after 100 mg/kg dosage via p.o. of DBK-1154. (B) Time-dependent Caspase-3/7 activation in E98 cells, after either DT-061 or DBK-1154 treatment (13 µM). Data shown are means from six replicates ± SD. (C) Time-dependent inhibition of cell viability in E98 cells, after either DT-061 or DBK-1154 treatment (13 µM). Data shown are means from six replicates ± SD. (D) Colony growth reduction after DBK-1154 treatment in GB cell lines in indicated concentrations. IC50 comparison between DBK-1154 and NZ-8-061 is shown in the insert. Data shown are means from four replicates ± SD. (E) Cell viability inhibition after DBK-1154 (5 µM) treatment in patient-derived primary glioma cells cultured in serum-free NSC medium. Data shown are means from six replicates ± SD. (F) Bioluminescence comparison on the day 14 during the orthotopic E98 in vivo model between vehicle or 100 mg/kg DBK-1154 treatment. Data shown are means from 8 vehicle and 10 DBK-1154-treated mice ± SEM, *P-value by Student’s t-test. (G) Survival of mice with orthotopic E98 xenografts after vehicle or 100 mg/kg DBK-1154 treatment, *P < 0.05 by Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test. Mice were randomized to two groups of 10 mice each based on bioluminescence signal before starting the treatment. Median survival was increased with DBK-1154 treatment from 15 to 26 days.